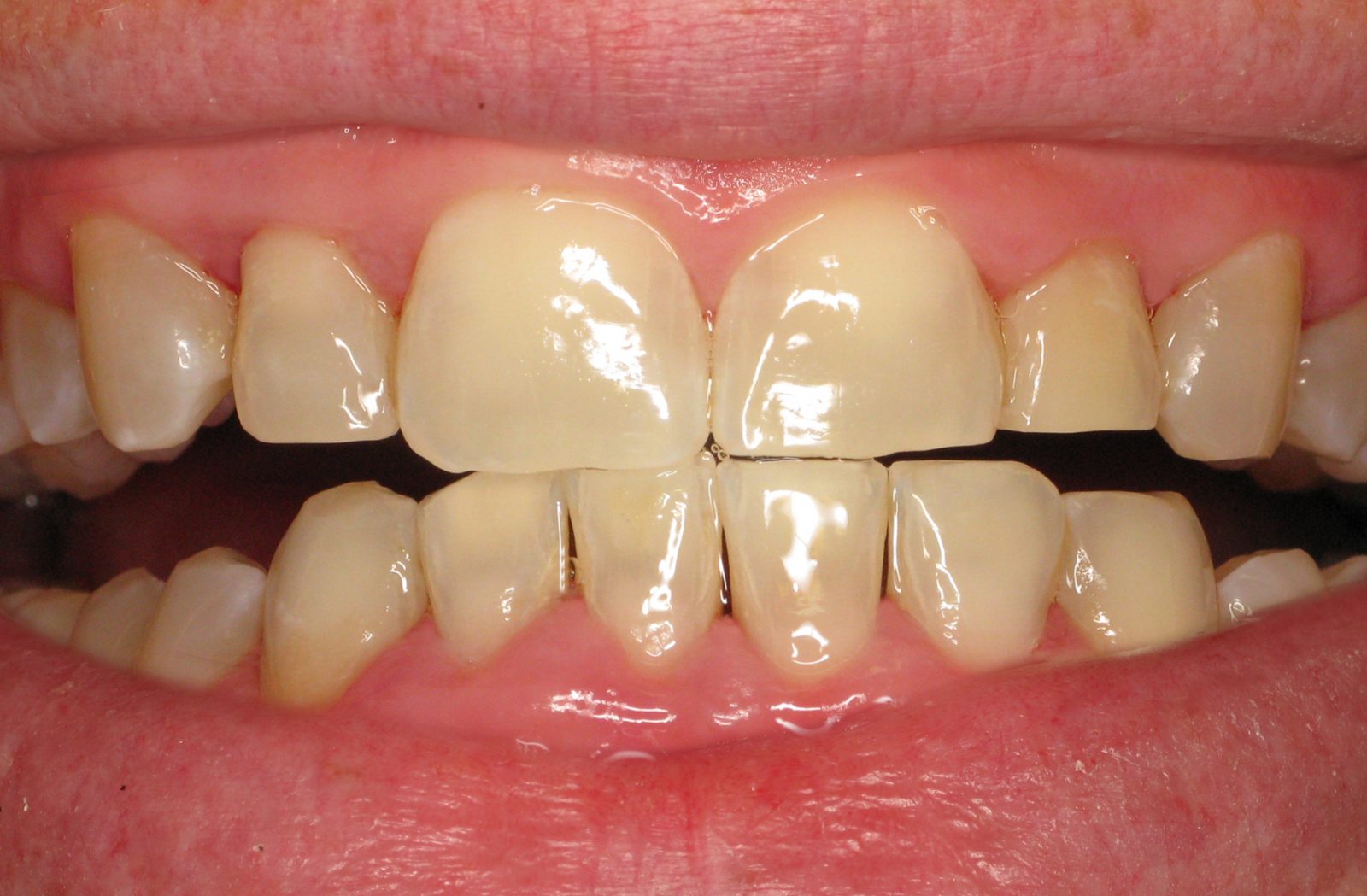
Gum Disease Symptoms: Redness
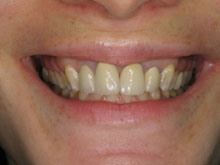
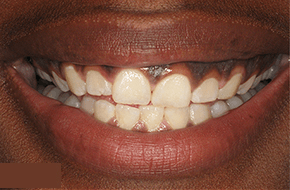
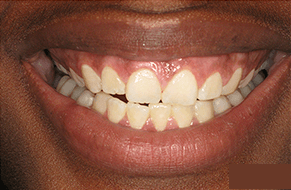
Gum disease symptoms often manifest in various ways, and redness is a prominent indicator of potential oral health issues. The presence of redness in the gums can signify the initial stages of gum disease, specifically gingivitis. This condition leads to inflammation and irritation of the gum tissues, causing them to appear red, swollen, and tender. Redness in the gums is often accompanied by bleeding during brushing or flossing. If left unaddressed, this early symptom can progress to more severe forms of periodontal disease.
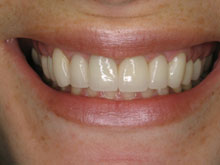
Our specialized expertise in treating gum disease symptoms ensures tailored care through procedures like laser periodontal therapy, reducing redness and preserving optimal gum health. Early detection and treatment of redness in the gums are pivotal in preventing the advancement of gum disease and safeguarding your oral well-being.
Does Gum Disease Cause Redness?
Redness in the gums is often a visible indication of gum disease, particularly in its early stage, known as gingivitis. Gum disease, caused primarily by plaque buildup along the gumline, triggers an inflammatory response in the gums, leading to redness, swelling, and tenderness. When bacteria in plaque accumulate and irritate the gums, it can cause them to appear red and inflamed. This condition can also result in bleeding during brushing or flossing. While redness in the gums is commonly associated with gingivitis, it’s essential to note that other factors, such as aggressive brushing, hormonal changes, or certain medications, can also cause gum redness. However, if redness persists or is accompanied by other symptoms like persistent bad breath or gum recession, it’s crucial to seek professional dental care.
What leads to bacterial plaque and tartar buildup in relation to gum disease?
Bacterial plaque and tartar buildup play pivotal roles in the development and progression of gum disease. Plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria, constantly forms on teeth due to the interaction between oral bacteria and food particles. When plaque is not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (also known as dental calculus) within 24-72 hours. Tartar is a hardened, calcified form of plaque that firmly adheres to the teeth and cannot be removed by standard oral hygiene practices alone.
This accumulation of plaque and tartar creates a favorable environment for bacteria to thrive along the gumline, leading to irritation, inflammation, and gum disease. Bacteria in plaque release toxins that irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and susceptible to bleeding. As gum disease progresses, plaque and tartar can lead to deeper pockets between the gums and teeth, further facilitating bacterial accumulation and causing damage to the gum tissues and underlying bone structures.
Regular and thorough dental hygiene, including brushing twice daily, flossing, and routine professional dental cleanings, are essential to prevent excessive plaque buildup and tartar formation. Moreover, dental professionals provide professional cleanings and scaling and root planing procedures to help remove tartar and plaque from hard-to-reach areas, minimizing the risk of gum disease progression and preserving optimal oral health.
How does gingival inflammation (gingivitis) contribute to redness in gum disease?
Gingival inflammation, commonly known as gingivitis, is a crucial contributor to the redness observed in gum disease. When plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria, accumulates along the gumline due to inadequate oral hygiene, it triggers an inflammatory response from the body’s immune system. The bacteria in plaque release toxins that irritate the delicate gum tissues, leading to inflammation, swelling, and redness.
As the body responds to the bacterial presence, blood flow to the affected area increases, causing the gums to appear red and inflamed. This redness is a visible sign of the body’s attempt to fight off the bacterial infection and indicates the early stage of gum disease. Alongside redness, individuals with gingivitis may experience tenderness and bleeding while brushing or flossing.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, leading to further inflammation, gum recession, and potential damage to the bone supporting the teeth. However, timely intervention through proper oral hygiene practices and professional dental care can effectively reverse gingival inflammation. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings help remove plaque and reduce inflammation, preventing the progression of gingivitis and promoting healthier gums. In advanced stages, treatments such as scaling and root planing or laser periodontal therapy, provided by specialists like those at Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery, can effectively manage and treat gingival inflammation, restoring gum health and preventing complications associated with gum disease.
How do poor oral hygiene practices influence gum redness?

Poor oral hygiene practices significantly impact gum health and can contribute to gum redness. When individuals neglect regular brushing, flossing, and proper oral care, bacterial plaque accumulates along the gum line and between teeth. This plaque comprises bacteria, food particles, and saliva, forming a sticky film that adheres to the teeth.
The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gums, triggering an inflammatory response from the body’s immune system. This inflammation manifests as redness, swelling, and tenderness in the gums. Without adequate oral hygiene, plaque buildup continues, exacerbating the irritation and leading to persistent gum redness.
Furthermore, neglecting routine oral care allows plaque to harden into tartar or dental calculus, which cannot be removed by regular brushing or flossing. Tartar accumulation further aggravates the gum tissues, causing increased redness and making it more challenging to maintain good oral health.
Poor oral hygiene practices create an environment conducive to bacterial growth and inflammation, increasing the risk of developing gingivitis or more severe forms of gum disease. Adopting proper oral hygiene habits—including brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings—is essential to prevent gum redness and associated oral health issues. These practices help remove plaque, prevent tartar buildup, and maintain healthy gums, reducing the likelihood of gum redness and mitigating the progression of gum disease.
What impact does smoking or tobacco use have on causing redness in gum disease?
Smoking and tobacco use have a detrimental impact on oral health and significantly contribute to the development and severity of gum disease, including redness in the gums. Tobacco products contain numerous harmful chemicals that compromise the body’s immune response, making it harder for the gums to fight infections.
Smoking or using tobacco products can cause a range of adverse effects on the gums, including:
- Reduced blood flow: Smoking constricts blood vessels, limiting blood flow to the gums. This diminished blood supply impairs the gums’ ability to receive nutrients and oxygen, hindering the body’s ability to combat infections and heal damaged tissues. Consequently, the gums become more susceptible to inflammation, leading to redness.
- Weakened immune response: Tobacco use weakens the immune system, making it less effective in fighting off bacterial infections, including those responsible for causing gum disease. This weakened immune response prolongs inflammation and delays the body’s ability to repair and regenerate gum tissues.
- Slower healing: Smoking can impede the healing process in the gums. Individuals who smoke often experience delayed recovery after dental procedures, making it more challenging for the gums to recover from the effects of gum disease.
- Increased risk of severe gum disease: Smokers have a higher risk of developing advanced stages of gum disease compared to non-smokers. This elevated risk includes more pronounced symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, and gum recession.
The combination of reduced blood flow, weakened immunity, slower healing, and increased susceptibility to infections due to smoking or tobacco use exacerbates gum disease symptoms, including redness in the gums. It’s crucial for individuals who smoke or use tobacco products to be vigilant about oral hygiene, seek regular dental check-ups, and consider quitting smoking to mitigate the progression of gum disease and improve oral health. Seeking guidance from dental professionals and implementing strategies to quit smoking can significantly benefit gum health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Are hormonal changes, specifically during pregnancy, linked to gum redness?
Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, are associated with an increased risk of gum redness and other oral health issues. The hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, particularly elevated levels of progesterone and estrogen, can affect the body’s response to plaque, making gums more sensitive to bacteria.
This hormonal shift can lead to a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis, characterized by gum inflammation, redness, swelling, and tenderness. These changes make pregnant individuals more prone to gum irritation and bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing.
Pregnancy gingivitis typically occurs in the second or third trimester and is more prevalent in individuals with poor oral hygiene habits. The increased blood flow to the gums during pregnancy and hormonal changes can exaggerate the body’s response to plaque and bacteria, resulting in heightened gum redness and inflammation.
Furthermore, if pregnancy gingivitis is left untreated, it may progress to more severe forms of gum disease. This highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, especially during pregnancy. Seeking professional dental care and guidance from a dentist or periodontist can help manage gum redness and prevent the progression of gum disease during this period.
Pregnant individuals should inform their dental care providers about their pregnancy to receive appropriate guidance and treatments tailored to their specific needs, ensuring optimal oral health for both the mother and the baby.
Experienced, professional gum treatment. Offices in New York City, Long Island, Nutley, New Jersey.
Free screening visits will include the following: Oral exam/cancer screening, periodontal evaluation, your possible treatment options, and estimated costs.