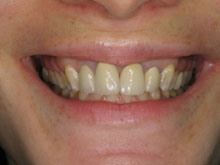
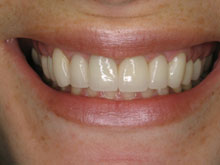
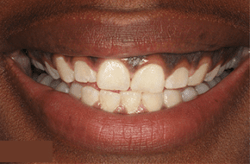
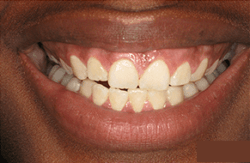
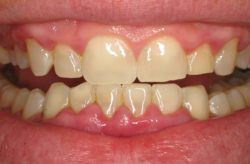
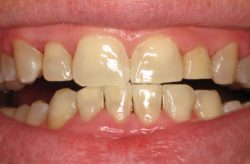
Stages Of Gum Disease

When it comes to oral health, people tend to focus heavily on the appearance of their teeth. However, the health and care of your gum tissue are just as important as preventing decay, stains, or cavities from your teeth. Protecting your gum tissue is vital to maintain a healthy smile.
People often think of gum disease, they think of it as one condition with a singular set of symptoms. This is actually not the case at all. Gum disease is a complex condition that, when left untreated, can progress to one of its advanced stages, leading to further dental complications.
If you believe you may be suffering from gum disease, you may be searching for some answers. You may want to seek information on how to recognize which stage of gum disease you may be suffering from, what actions you can take to prevent its progression, what are your treatment options, and which dental professionals you should seek.
When it comes to gum disease, you want to seek a dental professional that specializes in gum health, and our highly trained Periodontists do just that! Periodontists are dental specialists that are specialized in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease. Our main goal is to be an effective source of information when it comes to your gum and oral health and to provide our patients with the quality dental care they deserve. This includes knowing the different stages of periodontal disease and visiting our specialists early and regularly for maintenance check-ups.
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis
Technically, there are two forms of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is known as the earliest and mildest stage of gum disease. Symptoms can be reversed during this stage and are typically recognized by redness and inflamed gums. When gingivitis is left unchecked, it can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced case. Periodontitis is categorized into four stages:
- Periodontitis Stage 1: Initial
- Periodontitis Stage 2: Moderate
- Periodontitis Stage 3: Severe with Potential Tooth Loss
- Periodontitis Stage 4: Severe with Potential Loss of All Teeth
Each stage has its own set of signs and symptoms, which we will go into further detail.
Gingivitis
The first and most common stage of gum disease is gingivitis. Our mouths are full of bacteria from the foods and liquids we consume. The food particles and bacteria stick to the tooth’s surface and form what is known as plaque and tartar. Plaque is the sticky substance that coats the teeth if you do not brush and floss the teeth properly.
Plaque buildup is one of the main causes of gingivitis. When the buildup is not cleaned and stripped from the teeth and accumulates over time, it turns into a hardened substance known as calculus or tartar. When this formation of calculus occurs, your immune system will react to it and cause inflammation in the gums. There are also two forms of calculus:
- Supragingival Calculus. This means calculus is built above the gum line. This type of calculus appears yellow in color and forms from the minerals in your mouth. It is typically found between the front bottom teeth and is easily removed by our Periodontists.
- Subgingival Calculus. This is a more severe form of calculus that is more difficult to detect. It is found below the gum line and is black in color due to blood that is present from the inflammation. Subgingival calculus is more difficult to access and requires a more intensive treatment to remove.
Symptoms of gingivitis can be easy to ignore as they are minimal and painless. Gingivitis is the only stage of gum disease that can be cured. Proper brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups and cleanings can prevent gingivitis from advancing to the more serious stages of periodontitis.
Periodontitis and its Stages
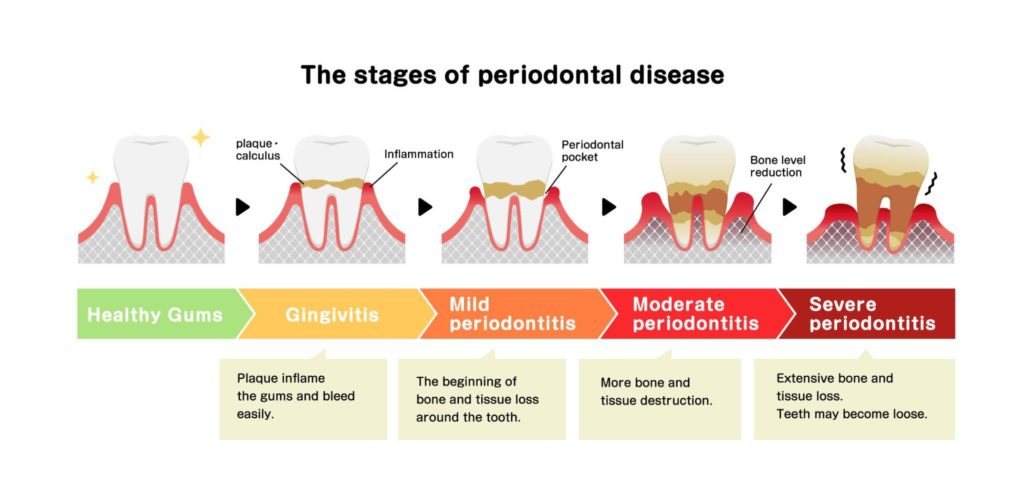
When gingivitis is left undetected and untreated, it advances to a stage known as periodontitis. This is when the plaque and calculus accumulate below the gum line and begin to affect the tooth’s root and jawbone. Once the disease reaches this stage, it begins to destroy the gum tissue and supporting bone matter. Periodontitis is categorized into four stages: initial, moderate, severe with potential tooth loss, and severe with potential for loss of all teeth.
Periodontitis Stage 1: Initial
When gingivitis worsens, it advances to the initial stage of periodontitis. During this stage, the symptoms become destructive. The plaque begins to accumulate below the gum line, and once it reaches this area, it releases toxins that stimulate chronic inflammation. You will not experience any pain during this stage. However, the inflammation is more severe than gingivitis, and bleeding will occur when you brush.
Unlike gingivitis, this stage is not reversible but is manageable by our Periodontitis and dental health team. The initial stage of periodontitis is treated by dental scaling and root planing. This is a deep cleaning that cleans and scrapes the bacterial debris from the affected areas below the gum line.
Periodontitis Stage 2: Moderate
The damages of the moderate stage of periodontitis are much more visible than the initial stage. The main difference between gum disease’s initial and moderate stages is gum recession and the formation of periodontal pockets. Gum recession is when the gum tissue begins to pull away from the tooth’s surface and exposes the root, creating space and gaps.
These spaces and gaps are known as periodontal pockets. These pockets can capture and hold harmful bacteria, causing damage to the jawbone. The jawbone is the supporting anchor for the teeth. Once the bacteria has compromised the jawbone, it will deteriorate over time. When left untreated, jawbone deterioration leads to tooth loss.
Periodontitis Stage 3: Severe with Potential Tooth Loss
Next, we enter stage 3, where you have a high potential for tooth loss during this stage. During this stage, the teeth appear longer due to excessive gum recession. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent bad breath or taste in the mouth.
- Teeth become loose and may shift because the gum tissue can no longer keep them firmly in place.
- Bite alignment changes due to migrating teeth.
- Soreness when biting on the teeth.
- Sensitivity to hot and cold liquids and beverages.
- Localized swelling or abscesses filled with pus.
Periodontitis Stage 4: Severe with Potential for Loss of All Teeth
The final stage of periodontitis is so severe with a potential loss of all teeth. Patients who reach this stage oftentimes already have multiple teeth missing. If your teeth have progressed so severely, there is no saving them. The only option at hand is to extract the affected teeth. Large gaps begin to form between the teeth, and the teeth no longer have the proper stability they need to withstand the force of your bite.
It is essential to seek treatment during this stage of periodontitis. Advanced periodontitis can lead to other serious health complications, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and several others. Once you reach this stage, these symptoms cannot be reversed. However, they can be managed. With the help and expertise of our Periodontists, we can sustain gum disease and effectively treat it, even at its latest stage.
Healthy Gum Tissue
It is important to remember that maintaining healthy gum tissue isn’t just beneficial for your oral health but for your overall health. Healthy gum tissue is smooth, firm, and pink in color. They fit tightly around the teeth, leaving no space or gaps in between teeth. There is no swelling or redness present.
You can prevent gingivitis from progressing to its advanced stages by creating and following an effective oral hygiene routine. Preventative and proper steps you can take are:
- Brushing your teeth with fluoride toothpaste for at least two minutes twice a day. You may want to invest in an electric toothbrush as they are more effective in removing plaque buildup.
- It is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to reduce irritation. It will also help to stimulate your gums gently.
- Brush along your gumline at a 45-degree angle to access the bacteria slightly underneath the gumline.
- Floss at least once a day.
- Use an anti-gingival mouthwash as part of your oral care twice a day.
- Avoid smoking tobacco. Tobacco smoking severely increases the bacteria and plaque in your mouth.
- Visit your dentist regularly for routine dental cleanings and check-ups. Dental specialists help to identify any complications early before they become serious.
Who is at Risk of Developing Gum Disease

No single case of gum disease is the same. Diagnosis and treatment are dependent on many components regarding the severity of the disease. There are several factors that may contribute to an increased risk of developing gum disease. It is important to let our dental professionals know your medical history and any potential risk factors so we can properly diagnose your case.
Smoking Tobacco
Smoking greatly increases your risk of gum disease. Many studies show that tobacco use is one of the main contributors to the progression and development of gum disease. The use of tobacco weakens the immune system making it more difficult for the body to fight gum disease infection.
Poor Oral Hygiene
A clean mouth is a healthy mouth. Without proper oral hygiene and regular dental wellness visits, bacteria can easily accumulate in the mouth and eventually progress to gum disease. Removing dental plaque and tartar regularly and thoroughly with the appropriate tooth-brushing and flossing products is essential in preventing gum disease.
Stress
Stress is also a risk factor for developing gum disease. It is linked to serious health complications, such as high blood pressure, cancer, and several others. Stress can hamper your body’s ability to fight off the infection that causes gum disease.
Other common risk factors that lead to periodontal disease include:
- Age
- Genetics
- Diabetes
- Certain medications
- Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause
Effects of Leaving Gum Disease Untreated
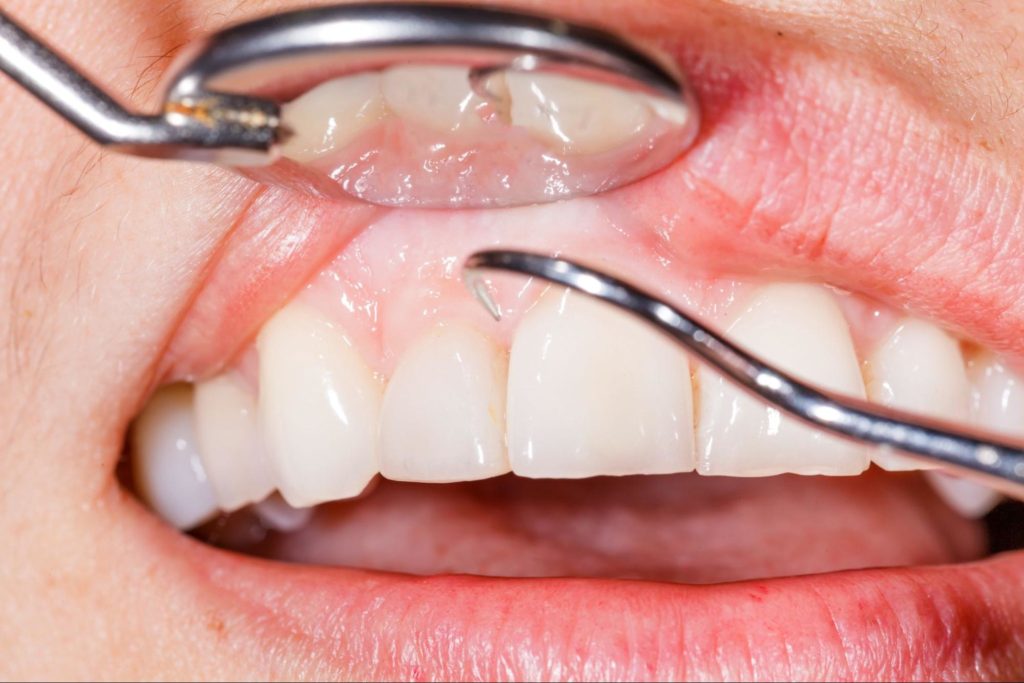
When gum disease is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, the most aggressive stage of gum disease. The infection and periodontal pockets deepen, which traps more harmful bacteria in hard-to-reach areas in the mouth. Once you reach this stage, the effects can result in jawbone damage and even tooth loss. The gums also begin to recede, pulling away from the teeth and jawbone surface and forming periodontal pockets.
Periodontal disease is manageable and can be reversed during its earliest stages with proper oral care and attending regular dental cleanings and checkups. However, it is nearly impossible to reverse once you have reached the advanced stages of periodontitis. As the bacteria accumulate, they can enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body, leading to other serious health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. It is vital to treat periodontal disease before it begins to affect your overall health.
Diagnosis From A Professional
Our dental professionals take pride in providing their patients with quality dental care. We strive to give each patient our undivided attention in order to diagnose and treat their case properly. We start by performing an oral examination. During the examination, we look for signs of gum bleeding, swelling, and if there is any teeth movement. We also measure the pocket depth to indicate if any periodontal pockets have formed. The larger and deeper the pocket, the more severe the case.
Our dental professionals also review your medical and oral history to see if you have any potential risk factors contributing to gum disease development. Common factors include smoking tobacco, diabetes, and a history of gum disease. A combination of these factors increases your risk even further.
Dental x-ray images help our Periodontists get a more accurate sense of the extent of your gum disease. With these images, we can view the condition of the jawbone to see if it has been compromised by the infection. Dental x-rays can also depict a more accurate depth of the periodontal pockets.
Treatment Options
Gum disease will continue to progress when left untreated. However, if diagnosed in time, the disease can be treated successfully. There are several treatment options that help remove, battle, and oftentimes eliminate the infection. Gum disease treatment may be nonsurgical or surgical depending on a number of factors:
- The severity of the infection.
- Oral health.
- Overall health.
- The capability of following post-treatment instructions and oral hygiene practices.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
We offer several non-surgical treatment options. Patients who suffer from the earliest stages of gingivitis benefit greatly from non-surgical therapies. Non-surgical gum disease treatments include:
Dental Scaling and Root Planing
Dental scaling is the first treatment step if your case is beyond gingivitis. Dental scaling goes much deeper than dental cleaning. Dental scaling involves carefully removing dental plaque and tartar buildup from the tooth’s surface and below the gum line. This process is known as deep cleaning. Our Periodontists will use a handheld tool known as a dental scaler and curette to scrape the plaque from the tooth’s surface gently. Your specialist will insert the tool between the gum line and the tooth to reach the plaque your normal toothbrush cannot access.
Dental root planing is the smoothing of the root surfaces in order to promote the reattachment of the gum tissue to the tooth. During this part of the procedure, our specialists will smooth the rough surfaces of the tooth root to provide a healthy surface for healing. Depending on the severity of the case, periodontal scaling and root planing may take more than one visit to treat the gum disease fully. Our specialists take the time to fully assess every patient to ensure they receive the quality dental care they deserve.
Laser-Assisted New Attachment (LANAP) Therapy
LANAP therapy is an innovative and minimally invasive treatment option for gum disease. This innovative technology allows our specialists to effectively and efficiently treat periodontal disease less invasively and with a shorter recovery time. Our specialists use the PerioLase laser to direct the pulsed laser at the affected gums. Our Periodontists will utilize a laser to target and remove the diseased tissue precisely. There is no need to worry about any scalpels to painfully remove the gum tissue.
Antibiotics
Antibiotic treatments come in several different forms. These forms include oral and topical antibiotics that are directly applied inside the gum pockets. Antibiotics are proven to help reduce inflammation and eliminate the bacterial growth that causes periodontitis. Antibiotic therapy is recommended for those who suffer from acute periodontal disease or gingivitis. There are stronger forms of antibiotics that are used more on patients who suffer from more advanced forms of periodontal disease. Common antibiotics used to treat the periodontal disease include:
- Tetracycline Antibiotics
- Amoxicillin
- Metronidazole
- Macrolide Antibiotics
- Azithromycin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Clindamycin
Surgical Treatment Options
Patients who suffer from more advanced stages of gum disease, such as moderate and advanced periodontitis, require surgical treatment. Surgical treatments for gum disease include:
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) is a regenerative technique that aims to repair periodontal defects so that the tooth or set of teeth has more stability and support. This procedure involves using a biocompatible membrane material, often combined with a bone graft, that promotes the growth of lost tissue and bone around the tooth’s surface.
Flap Surgery
Flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery is a more invasive version of dental scaling and root planing. During flap surgery, scalpels are used to make incisions to lift back the gum tissue and expose the tartar buildup. The tartar is then removed, and in some complicated cases, the irregular surfaces are smoothed out to prevent disease-causing bacteria from producing in those rough areas.
We then place the gum tissue tightly against the tooth aiming to reduce the space between the two areas. This open space is known as a pocket. Eliminating this pocket space is also done to reduce any open areas where harmful bacteria can grow and lead to periodontal disease.
Soft Tissue Grafting
Soft tissue grafting is necessary to treat gum recession. This procedure supports thin gums or fills in spaces where gum recession is present. Our specialists will take soft tissue grafts, normally from the roof of the mouth, and stitch the tissue into place over the affected area. We administer a local anesthetic to our patients during the procedure to provide comfort. The main types of soft tissue grafting include:
-
- Connective Tissue Grafting
- Free Gingival Grafts
- Pedicle Grafts
Dental Bone Grafting
Dental bone grafting is an extremely common procedure that adds thickness and volume to your jaw in areas where bone deterioration has occurred. The bone graft material is normally taken from your own body, which is called autogenous, or in some instances, it may be retrieved from a human tissue bank, known as allografting. The different forms of bone grafting include:
-
- Socket Preservation
- Ridge Augmentation
If you are nervous about your teeth and gum health or are experiencing any symptom related to gum disease, we are here to help! Our experienced dental professionals strive to help our patients be and feel their best through compassionate and comprehensive dental care. We also ensure to educate our patients on dental conditions, such as periodontal disease. Schedule your consultation by calling (877) 440-3564. Our Periodontists will perform a full mouth examination and discuss your best treatment options!
FAQ
What are the leading causes of gum?
The leading causes of gum disease are dental plaque and tartar formation. Not correctly brushing and flossing can cause small bacteria buildup in the form of a sticky white film on the teeth or in the junction between the tooth and gum. Gum disease may affect you if this combines with one or two risk factors.
Who is most at risk for gum disease?
A smoker, an obese person, and those who ignore oral hygiene risk gum disease. Also, age is a risk factor for gum disease. According to the CDC data, 70% of people 65 years and older have some type of gum disease.
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can lead to severe periodontitis and become more noticeable in a matter of weeks. Depending on the risk factors, periodontitis may lead to pain and tooth or periodontal tissue deterioration in a couple of months or a few years. It would only be best resolved with extraction and/or surgery.
What three risk factors may make someone more likely to develop gum disease?
The three most common risk factors for gum disease include inadequate oral hygiene, tobacco smoking, and diabetes.
Who is most at risk for gum disease?
A smoker, an obese person, and those who ignore oral hygiene risk gum disease. Also, age is a risk factor for gum disease. According to the CDC data, 70% of people 65 years and older have some type of gum disease.
Is gum disease reversible?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease, where the gums are inflamed due to bacterial buildup along the gumline. The damage occurring at this stage can be reversed since the supporting bone and tissue have not been compromised.