Osseous Surgery
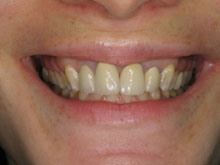
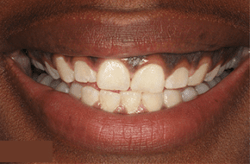
Traditionally, gum disease has been treated by trimming away infected gum tissue and re-contouring the uneven bone tissue. Although this is still an effective way of treating gum disease, new and more sophisticated procedures are used routinely today, such as osseous surgery, or pocket reduction.
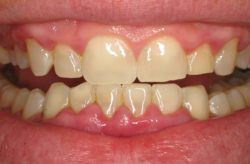
Healthy bone and gum tissue fit snugly around the teeth. When you have periodontal disease, this supporting tissue and bone is destroyed, forming “pockets” around the teeth.
Over time, these pockets deepen, providing a larger space for bacteria to live and grow. As bacteria develop around the teeth, they can accumulate and advance beneath the gum tissue. These deep pockets collect even more bacteria, resulting in further bone and tissue loss. Eventually, if too much bone is lost, there will not be enough support for the teeth, and they will need to be extracted.
-
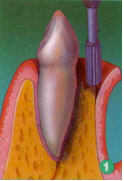
The gum is lifted from the tooth and bone, and diseased tissue is removed. The uneven bone may also may be reshaped. -
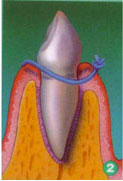
After surgery, the gum is repositioned and sutured in place.
What Is Osseous Surgery?
During this procedure, your gum tissue is folded back, so that disease-causing bacteria may be removed from the pockets, and then the tissue is secured back into place. In some cases, irregular surfaces of damaged bone are smoothed to limit places in which disease-causing bacteria can hide. Removing the bacteria allows the gum tissue to better attach to healthier, bacteria-free bone.
In order to prevent infections such as periodontal disease, the attachment between the gums and teeth need to be tight together. When large gaps develop in between the gums and tooth, it provides space for bacteria to spread and manifest. In order to determine if surgery is needed, our specialists will measure the pocket depth of each tooth utilizing a periodontal probe. Healthy gum tissue attachment should measure no more than three millimeters deep. Measurements of four millimeters or more may indicate bone loss.
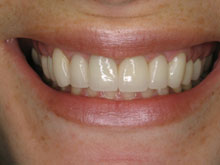
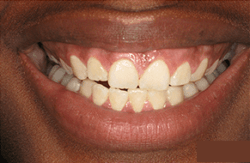
If a large packet does not respond to treatment, such as scaling or root planning, osseous surgery is necessary to treat the area. The surgery will reduce the pocket size, strengthen the gums, and remove and prevent future bacteria build up.
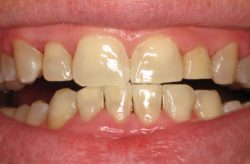
Reducing pocket depth and eliminating existing bacteria are important to stop the decaying process and to prevent further damage caused by the progression of periodontal disease and, of course, to help you maintain a healthy smile. Osseous surgery is often the first step in fighting periodontal disease. It is important to note, however, that eliminating bacteria alone may not be sufficient to prevent disease recurrence. When pockets become very deep, they are more difficult for you and your dental care professional to clean, so it’s important for you to maintain good oral hygiene after the procedure. A combination of reduced pocket depth, daily oral hygiene, and professional periodontal maintenance increases your chances of keeping your natural teeth and decreases the chance of serious health problems associated with periodontal disease.
The length of recovery time depends on the severity of the periodontal disease and your overall health. Following the procedure, you can expect to experience mild discomfort and slight bleeding of the gums. It is important to follow the guidelines instructed by our specialists. It is important to avoid vigorous brushing or rinsing near the surgical area. Prior to the surgery, it is recommended to maintain a soft food diet to prevent any trauma on the affected areas.
During osseous surgery the patient will be under local anesthesia, therefore, no pain is felt during the procedure. Most patients experience mild to moderate pain after osseous surgery that can be managed with over the counter pain relievers.