In-Depth Look at Gingival Grafting: Procedures, Techniques, and Outcomes
Introduction to Gingival Grafting
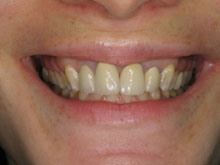
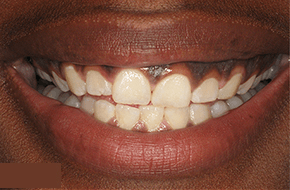
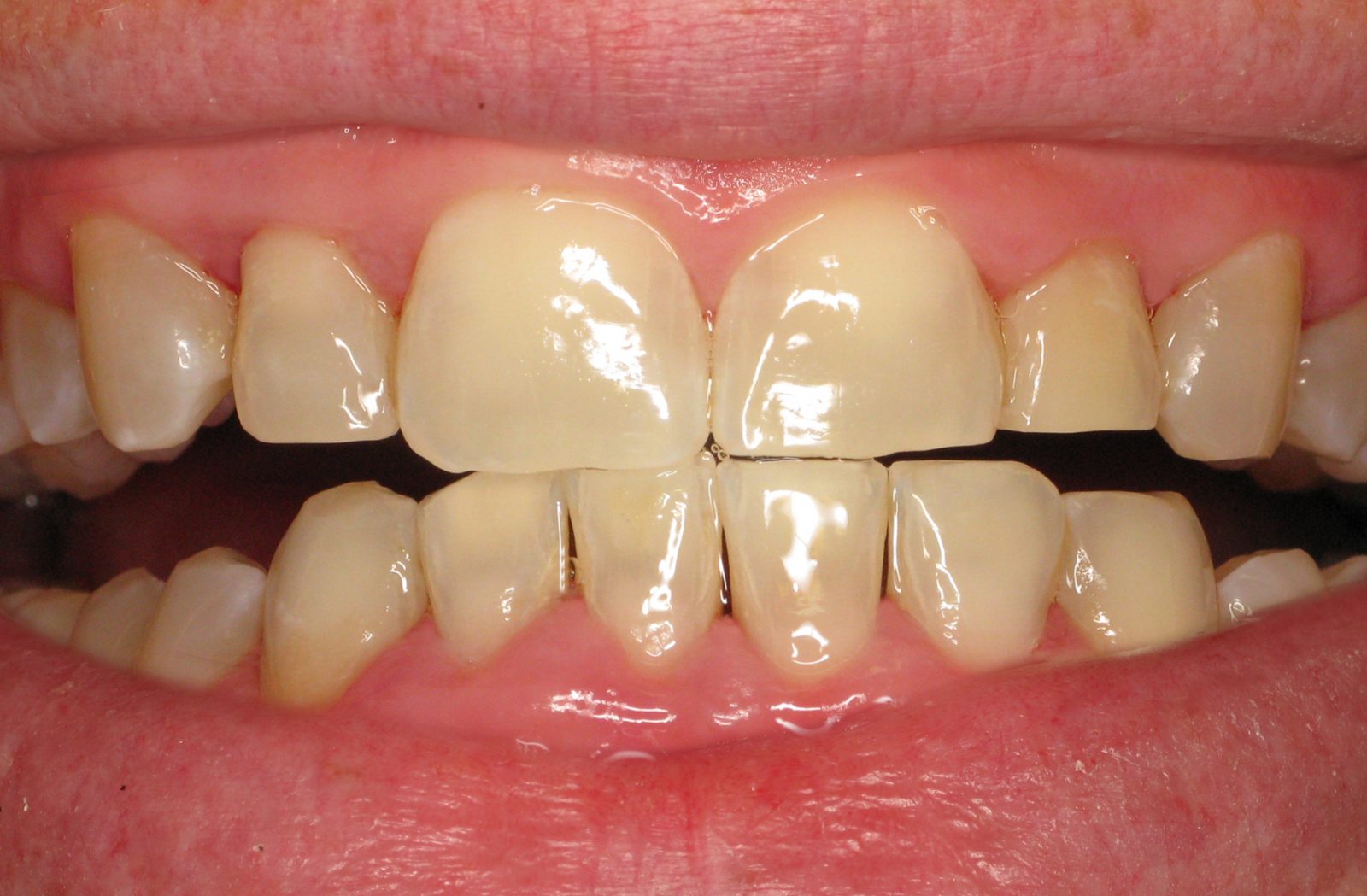
If you are looking for a solution to receding gums or want to enhance the appearance of your smile, you’ve come to the right place. Gingival grafting is a specialized dental procedure that addresses gum recession, a common issue that can lead to tooth sensitivity, root exposure, and an unbalanced smile.
Gingival grafting, also known as gum grafting or periodontal plastic surgery, involves the transfer of healthy gum tissue from one part of your mouth to another. The procedure aims to restore the gum line, protect tooth roots, and improve the overall aesthetics of your smile. It is typically performed by a periodontist or a dentist with advanced training in gum treatments.
Our experienced team of dental professionals here at Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery understands the impact of receding gums on oral health and self-confidence. Through gingival grafting, we can help you regain a healthy gum line and achieve a more harmonious smile.
Take the first step towards improving your gum health and smile aesthetics. Continue reading our page to learn more, and contact us today at (877) 440-3564 to schedule a consultation with our skilled team. Let us help you achieve the healthy, beautiful smile you deserve through gingival grafting.
Definition and Importance of Gingival Grafting in Periodontics
Gingival grafting plays a crucial role in periodontics, focusing on the health and treatment of the supporting structures of teeth, particularly the gums. This specialized procedure involves transplanting gum tissue to areas where the recession has occurred or where additional tissue is needed to improve aesthetics or protect the underlying tooth structure.
Gingival grafting serves multiple purposes. It addresses gum recession, which can result from factors such as aggressive brushing, periodontal disease, or genetic predisposition. Receding gums compromise one’s smile and expose vulnerable tooth roots, leading to heightened tooth sensitivity and an increased risk of root decay. By grafting healthy gum tissue onto the affected areas, the procedure helps to restore a proper gum line, protect the roots, and prevent further recession.
Secondly, gingival grafting contributes to the overall health of the gums. Healthy gums are essential for maintaining strong and stable teeth. They act as a protective barrier against bacteria, preventing their entry into the underlying bone and supporting structures. Gingival grafting promotes a healthier oral environment and reduces the risk of future periodontal issues.
Gingival grafting enhances the aesthetics of the smile. Receding gums can make teeth appear longer, uneven, or asymmetrical, detracting from the overall beauty of one’s smile. By restoring a balanced and harmonious gum line, gingival grafting helps improve the teeth’s appearance, resulting in a more confident and appealing smile.
The Evolution and Progress of Gingival Grafting Techniques
Gingival grafting techniques have evolved significantly, improving outcomes and patient satisfaction. The development of these techniques can be attributed to advancements in dental research, technology, and a better understanding of the biology of gum tissue.
Traditionally, gingival grafting involved the use of autografts, where the tissue was harvested from the patient’s palate and transplanted to the recipient site. While effective, this approach had limitations, such as limited availability of donor tissue and increased patient discomfort and healing time.
Alternative grafting techniques have emerged in recent years, offering more options and benefits. One such technique is the use of allografts, where donor tissue from a tissue bank is utilized. Allografts eliminate the need for harvesting tissue from the patient, reducing post-operative pain and morbidity. Additionally, xenografts, which use animal-derived tissue, have also been explored as an option for gingival grafting.
Another significant advancement is the development of synthetic grafting materials, such as collagen-based substitutes. These materials provide a scaffold for tissue regeneration and can be combined with growth factors to enhance healing and promote the integration of new gum tissue.
Furthermore, advancements in surgical techniques, such as tunneling and microsurgical approaches, have allowed for more precise and minimally invasive grafting procedures. These techniques reduce post-operative discomfort, faster healing, and improved aesthetics.
Role of Gingival Grafting in Oral Health and Aesthetics
Gingival grafting plays a vital role in both oral health and aesthetics, contributing to the overall well-being and appearance of an individual’s smile.
In terms of oral health, gingival grafting addresses the issue of gum recession. Receding gums expose the sensitive root surfaces of teeth, making them susceptible to damage, decay, and increased sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli. By grafting healthy gum tissue onto the affected areas, gingival grafting helps to restore a proper gum line, covering and protecting the exposed roots. This process reduces tooth sensitivity, minimizes the risk of root decay, and promotes a healthier oral environment.
Additionally, gingival grafting supports periodontal health by improving the condition of the gum tissues. Healthy gums are crucial for maintaining strong and stable teeth. They act as a protective barrier against bacteria and prevent the progression of periodontal disease, which can lead to bone loss, tooth mobility, and tooth loss. By reinforcing the gum line and addressing gum recession, gingival grafting helps to preserve and enhance the health of the supporting structures of the teeth.
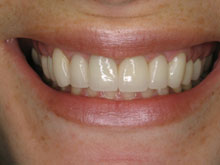
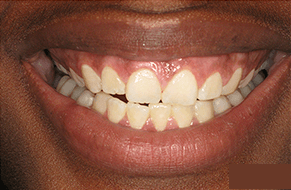
From an aesthetic standpoint, gingival grafting plays a significant role in enhancing the smile’s appearance. Receding gums can make the teeth appear longer, uneven, or asymmetrical, affecting self-confidence and overall smile aesthetics. Gingival grafting creates a more pleasing and natural-looking smile by restoring a balanced and harmonious gum line. The procedure helps to develop proper tooth proportions, improves smile symmetry, and enhances the overall esthetics of the teeth and gums.
Understanding the Need for Gingival Grafting
Understanding the need for gingival grafting is crucial for individuals who experience gum recession or want to improve their smile aesthetics. By recognizing the signs and reasons for undergoing this procedure, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their oral health and overall well-being.
Gum recession is a common issue resulting from various factors, including aggressive brushing habits, periodontal disease, hormonal changes, genetic predisposition, or the natural aging process. It is characterized by the gradual loss of gum tissue, which exposes the sensitive roots of the teeth and creates an uneven gum line. Receding gums pose oral health risks and can affect one’s self-confidence and smile aesthetics.
Gingival grafting becomes necessary when gum recession reaches a point where it compromises the health and function of the teeth. Exposed tooth roots become susceptible to decay, sensitivity, and damage. Furthermore, gum recession can lead to an unbalanced smile, making the teeth appear longer or unevenly spaced.
By undergoing gingival grafting, individuals can address these concerns. The procedure involves transplanting healthy gum tissue to areas of recession or aesthetic concern, effectively restoring a proper gum line, protecting the roots, and enhancing the smile’s overall appearance.
It is essential to consult with a qualified periodontist or dentist to determine the need for gingival grafting. They can assess the extent of gum recession, evaluate oral health conditions, and discuss treatment options based on individual circumstances and goals.
Ultimately, understanding the need for gingival grafting empowers individuals to take proactive steps to maintain their oral health, prevent further complications, and achieve a confident, healthy smile. If you want to correct your smile and believe gingival grafting is a suitable option, call (877) 440-3564 to schedule an appointment and consult our highly skilled Periodontists.
Causes and Consequences of Gingival Recession
Gingival or gum recession can have various causes and consequences that impact oral health and aesthetics. Understanding these factors is essential for recognizing the importance of addressing gingival recession promptly.
Causes of Gingival Recession:
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can contribute to gum tissue abrasion and recession.
- Periodontal Disease: Gum disease, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, is a leading cause of gingival recession. The infection and inflammation can weaken and damage the gum tissues, leading to recession.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to having thinner or weaker gum tissues, making them more susceptible to recession.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, increasing the risk of gum disease and subsequent recession.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can make gums more sensitive and prone to recession.
Consequences of Gingival Recession:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed tooth roots are more sensitive to temperature changes and certain foods or drinks, causing discomfort or pain.
- Increased Risk of Decay: With receding gums, the tooth roots become exposed, lacking the protective enamel layer. This increases the susceptibility to tooth decay and cavities.
- Gum Inflammation and Infection: The exposed tooth roots are more vulnerable to bacterial plaque accumulation, leading to gum inflammation and potential infections.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Gingival recession can cause an uneven gum line, making the teeth appear longer and resulting in an aesthetically unpleasing smile.
- Tooth Mobility and Loss: Advanced gum recession can lead to bone loss and, ultimately, tooth mobility or even tooth loss if left untreated.
Addressing gingival recession through treatments like gingival grafting can help mitigate these consequences. It restores gum tissue, covers exposed roots, reduces sensitivity, improves oral health, and enhances the overall aesthetics of the smile. It is essential to consult with a dental professional to determine the underlying cause of the gingival recession and develop an appropriate treatment plan to prevent further complications and maintain optimal oral health—call (877) 440-3564 to schedule your appointment with one of our specialists.
Impact of Gingival Recession on Oral Health and Aesthetics
Gingival recession significantly impacts oral health and aesthetics, affecting various aspects of the mouth and overall appearance.
Impact on Oral Health:
- Increased Sensitivity: Receding gums expose sensitive tooth roots, leading to heightened sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures and certain foods. This can cause discomfort or pain during eating or drinking.
- Vulnerability to Decay: When the roots are exposed due to gingival recession, they lack the protective enamel layer, increasing the risk of tooth decay and cavities.
- Gum Inflammation and Infection: Exposed tooth roots are more susceptible to bacterial plaque accumulation, leading to gum inflammation (gingivitis) and potentially progressing to periodontal disease (periodontitis). This can result in gum swelling, redness, tenderness, and even gum abscesses.
- Gum Pocket Formation: Gingival recession often leads to gum pockets or deep spaces between the teeth and gums. These pockets provide a breeding ground for bacteria and can further contribute to gum disease and bone loss.
- Root Exposure and Damage: With receding gums, the roots are exposed and vulnerable to mechanical damage, such as abrasion, erosion, or trauma. This can lead to further complications and compromise the integrity of the teeth.
Impact on Aesthetics:
- Uneven Gum Line: Gingival recession can result in an uneven gum line, where certain teeth may appear longer or more exposed than others. This can create an aesthetically unpleasing smile.
- Tooth Length and Proportions: Receding gums can make the teeth appear longer, affecting their natural length and proportions. This can create an imbalanced smile and diminish overall smile aesthetics.
- Smile Harmony: The presence of gingival recession can disrupt the harmony and symmetry of the smile, affecting its overall attractiveness.
- Self-Confidence: The visible effects of gingival recession, such as tooth sensitivity, uneven gum line, or exposed roots, can lead to decreased self-confidence and self-esteem when smiling or interacting with others.
Identifying Candidates for Gingival Grafting
Identifying suitable candidates for gingival grafting involves evaluating individuals experiencing gum recession or seeking to improve their smile aesthetics. Assessing the candidacy for this procedure requires considering various factors related to oral health and individual needs. Those factors include:
- Gum Recession: Candidates for gingival grafting typically have significant gum recession, where the tooth roots are exposed or an uneven gum line. Gum recession can lead to oral health issues, such as tooth sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and compromised aesthetics.
- Oral Health Status: Candidates should have a healthy mouth free of active gum disease or other significant dental conditions. Addressing any existing oral health issues before undergoing gingival grafting is essential for optimal treatment outcomes.
- Adequate Gum Tissue Donor Sites: Gingival grafting involves obtaining healthy gum tissue from a donor site (often the patient’s own palate or alternative sources). Candidates should have sufficient gum tissue available for harvesting without compromising the health or aesthetics of the donor site.
- Motivation and Commitment: Candidates must maintain proper oral hygiene practices and follow post-operative care instructions provided by their dental professional. Good oral hygiene habits and regular dental visits are essential for the long-term success of gingival grafting.
- Desired Aesthetics: Candidates concerned about their smile’s appearance due to gum recession or an uneven gum line can be potential candidates for gingival grafting. Restoring a natural and harmonious gum line can significantly enhance the overall aesthetics of their smile.
- Health Considerations: Our dental professionals will assess the candidate’s general health. Certain medical conditions or medications may affect the suitability or success of the procedure. Collaboration with the candidate’s healthcare provider may be necessary in such cases.
Ultimately, the decision regarding the candidacy for gingival grafting is made through a comprehensive evaluation by one of our qualified dental professionals. They will consider the individual’s circumstances, oral health status, and treatment goals to determine if gingival grafting is the appropriate solution to address their gum recession and achieve optimal oral health and aesthetics.
Assessment and Diagnosis of Gingival Recession
The assessment and diagnosis of gingival recession involve a comprehensive evaluation of the gum tissues to determine the extent of the recession and the underlying causes.
During an oral examination, a dentist or periodontist carefully examines the gums and measures the depth of the gum pockets around each tooth. This measurement helps assess the severity of gum recession and any associated periodontal disease. Additionally, the dentist examines the teeth and roots for signs of sensitivity, decay, or damage resulting from exposed root surfaces.
The evaluation process also involves assessing potential contributing factors to the gingival recession. This includes reviewing the patient’s oral hygiene practices, brushing technique, presence of gum disease, genetic predisposition, hormonal factors, and any previous dental treatments or trauma that may have affected the gums.
In some cases, dental X-rays or other imaging techniques may be utilized to evaluate bone levels and determine if underlying bone loss has occurred.
Based on the assessment findings, a diagnosis of gingival recession is made, accompanied by identifying the potential causes and contributing factors. This helps develop an appropriate treatment plan, including gingival grafting or other interventions to address the gum recession, alleviate symptoms, and improve oral health and aesthetics.
It is essential to consult with a dental professional for a thorough assessment and accurate diagnosis of gingival recession. This allows for personalized treatment recommendations and appropriate measures to prevent further progression of gum recession and associated complications.
Techniques in Gingival Grafting
Gingival grafting encompasses various techniques to restore and enhance gum tissue in cases of gum recession. These techniques include free gingival grafts, connective tissue grafts, pedicle grafts, and acellular dermal matrix grafts. Each method offers unique advantages and is tailored to individual patient needs. The free gingival graft involves harvesting a thin layer of tissue from the palate and grafting it onto the recipient site to augment the gum tissue. Connective tissue grafts utilize a similar approach but include the underlying connective tissue for better root coverage. Pedicle grafts involve transferring adjacent gum tissue to cover the exposed root surface while maintaining its blood supply. Lastly, acellular dermal matrix grafts utilize processed human or animal tissue to scaffold new gum tissue growth. Understanding these techniques is crucial for patients and dental professionals in determining the most suitable approach to address gum recession and achieve optimal oral health and aesthetics.
Free Gingival Graft
The free gingival graft is a surgical technique used in periodontics to address gum recession and increase the thickness of the gum tissue. It involves harvesting a small piece of tissue, typically from the patient’s palate (roof of the mouth), and transplanting it to the recipient site where gum recession has occurred.
Procedure, Recovery, and Outcome of Free Gingival Graft
Here is an overview of the steps involved in the free gingival graft procedure:
- Anesthesia: The patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the graft will be taken from (palate) and the recipient site.
- Graft Harvesting: A small, rectangular-shaped piece of tissue is carefully removed from the palate. The donor tissue is selected based on its thickness and compatibility with the recipient site.
- Recipient Site Preparation: The gum recession or thinning area is thoroughly cleaned and prepared to receive the graft. The exposed root surface may also be cleaned and smoothed if necessary.
- Graft Placement: The harvested tissue is then positioned over the recipient site, covering the exposed root surface. The graft is secured in place using sutures or other fixation techniques. The graft acts as a protective barrier and provides a foundation for new gum tissue growth.
- Postoperative Care: After the procedure, the patient will receive specific instructions for postoperative care. This may include guidelines for pain management, oral hygiene, dietary restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
During the healing process, the transplanted tissue integrates with the existing gum tissue and blood supply, promoting the growth of new cells and improving the thickness and coverage of the gum tissue. Over time, the grafted tissue blends in with the surrounding gums, providing a healthier and more aesthetically pleasing gum line.
The free gingival graft technique effectively treats gum recession, reduces tooth sensitivity, prevents further recession, and improves overall periodontal health. It is essential to consult with a qualified dental professional who can assess your specific needs and determine if a free gingival graft or alternative treatment approach is most appropriate for you.
Connective Tissue Graft
The connective tissue graft is a surgical technique commonly employed in periodontics to address gum recession and restore gum tissue in areas where the roots of the teeth are exposed. This procedure involves harvesting a small piece of connective tissue from beneath the surface of the palate or a nearby donor area and using it to augment the recipient site.
Procedure, Recovery, and Outcome of Connective Tissue Graft
Here is a breakdown of the steps involved in a connective tissue graft procedure:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the areas involved, including the palate (if the tissue is taken from there) and the recipient site.
- Graft Harvesting: A small incision is made in the palate, and a thin layer of connective tissue is carefully removed from beneath the surface. The incision is then sutured.
- Recipient Site Preparation: The area experiencing gum recession is cleaned and prepared to receive the graft. This involves making incisions to create a small pouch or tunnel to accommodate the graft.
- Graft Placement: The harvested connective tissue is positioned over the exposed root surfaces within the prepared pouch or tunnel. The tissue is secured using sutures, ensuring it covers the recession area and adheres properly to the existing gum tissue.
- Postoperative Care: Following the procedure, the patient receives postoperative care instructions. These instructions may include guidelines for pain management, oral hygiene practices, dietary restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
Over time, the transplanted connective tissue integrates with the surrounding gum tissue, creating a thicker and healthier gum attachment. The connective tissue graft helps to cover the exposed root surfaces, reduce tooth sensitivity, improve the aesthetics of the gum line, and enhance overall periodontal health.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified periodontist or dental professional to determine if a connective tissue graft is the appropriate treatment option for your specific gum recession concerns. They will evaluate your oral health and customize the procedure to address your individual needs effectively.
Pedicle Graft
The pedicle graft, also known as the lateral sliding graft or the rotational flap, is a surgical technique used to treat gum recession by utilizing nearby gum tissue. Unlike other grafting methods involving tissue from a different donor site, the pedicle graft consists in transferring a portion of gum tissue from an adjacent area to cover the exposed root surface.
Procedure, Recovery, and Outcome of Pedicle Graft
Here is an overview of the steps involved in a pedicle graft procedure:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the areas involved, including the donor and recipient sites.
- Donor Site Selection: The dentist or periodontist identifies a suitable donor site within the patient’s mouth, typically an area adjacent to the location of gum recession. The chosen donor site has healthy gum tissue that can easily move to cover the exposed root surface.
- Tissue Displacement: A small incision is made near the donor site, and the gum tissue is carefully separated from the underlying bone, creating a flap. The flap is then rotated or slid over the recession site to cover the exposed root surface.
- Suturing: The flap of gum tissue is secured in its new position using sutures. The sutures help hold the tissue in place during the healing process.
- Postoperative Care: The patient receives postoperative care instructions, which may include guidelines for pain management, oral hygiene practices, dietary restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
During the healing process, the blood supply to the pedicle graft remains intact because the tissue is still connected to its original blood vessels. This ensures the survival and integration of the grafted tissue with the surrounding gum tissue. Over time, the grafted tissue covers the exposed root surface, improving aesthetics, reducing tooth sensitivity, and preventing further gum recession.
The suitability of a pedicle graft depends on the individual’s specific case and the availability of healthy adjacent gum tissue. A thorough examination by a dental professional will determine if a pedicle graft is the appropriate treatment option to address gum recession and promote gum tissue regeneration.
Acellular Dermal Matrix Graft
The acellular dermal matrix (ADM) graft is used in periodontics and oral surgery to restore gum tissue and treat gum recession. Unlike other grafting procedures that use a patient’s tissue, the ADM graft utilizes processed human or animal tissue as a scaffold for gum tissue regeneration.
Procedure, Recovery, and Outcome of Acellular Dermal Matrix Graft
Here is an overview of the steps involved in an acellular dermal matrix graft procedure:
- Graft Selection: The dentist or periodontist selects an acellular dermal matrix graft from a reputable source. These grafts are derived from human or animal tissue that has been processed to remove cells, leaving behind a supportive extracellular matrix.
- Recipient Site Preparation: The area with gum recession is cleaned and prepared for graft placement. The exposed root surface may be cleaned and smoothed if necessary.
- Graft Placement: The acellular dermal matrix graft is trimmed to fit the size and shape of the recession area. It is then carefully positioned over the exposed root surface and sutured. The graft acts as a scaffold, providing a framework for new gum tissue growth.
- Suturing and Healing: The graft is secured using sutures to ensure stability and proper integration. Over time, the patient’s own cells migrate into the acellular dermal matrix, repopulating the graft with new blood vessels and gum tissue.
- Postoperative Care: The patient receives postoperative care instructions, which may include guidelines for pain management, oral hygiene practices, dietary restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
The acellular dermal matrix graft serves as a framework for the patient’s own cells to regenerate and populate the area, ultimately resulting in increased gum tissue thickness and improved root coverage. It can effectively treat gum recession, enhance aesthetics, reduce tooth sensitivity, and provide long-term stability.
One of the advantages of using ADM grafts is that they eliminate the need for a donor site, reducing the surgical invasiveness and discomfort associated with harvesting tissue from the patient’s own body. Additionally, ADM grafts have a controlled and predictable composition, allowing for better graft integration and healing.
It is essential to consult with a qualified dental professional who can evaluate your specific case and determine if an acellular dermal matrix graft is the appropriate treatment option for your gum recession and oral health needs.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care in Gingival Grafting
Preoperative and postoperative care is crucial for successful and optimal healing of gingival grafting procedures. Following these care instructions helps minimize discomfort, reduce the risk of complications, and promote proper recovery. Here is an overview of the preoperative and postoperative care involved in gingival grafting:
Preoperative Care:
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain excellent oral hygiene by brushing your teeth gently and flossing regularly before the procedure.
- Medications: Inform your dentist about any medications, supplements, or medical conditions you have to ensure proper adjustments are made, if necessary.
- Diet: Follow any specific dietary instructions your dentist provides, such as avoiding food and drinks for a specific period before the surgery if required.
Postoperative Care:
- Oral Hygiene: Follow the dentist’s instructions for postoperative oral hygiene, including using a prescribed mouth or gentle saltwater rinse. Brush your teeth gently, avoid the surgical area, and resume flossing as your dentist directs.
- Pain Management: Take any prescribed pain medication as directed or use over-the-counter pain relievers as your dentist recommends to manage any discomfort or pain.
- Swelling and Ice Packs: Apply ice packs outside your face near the surgical area for the first 24-48 hours to help minimize swelling.
- Diet: Stick to a soft or liquid diet for a few days after the procedure to avoid placing unnecessary pressure on the graft site. Gradually reintroduce solid foods as advised by your dentist.
- Rest and Physical Activity: Limit physical activity and strenuous exercise for the first few days for proper healing.
- Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your dentist to monitor the healing process, remove any stitches if necessary, and assess the overall success of the graft.
It’s essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your dentist or periodontist, as they may vary based on individual circumstances and the type of graft performed. By adhering to preoperative and postoperative care guidelines, you can promote a smooth recovery and maximize the effectiveness of your gingival grafting procedure.
Preparing for Gingival Grafting: Patient Guidelines
Preparing for gingival grafting involves following specific guidelines to ensure a successful procedure and optimal healing. Here are some patient guidelines to consider:
- Consultation and Communication: Schedule an initial consultation with your dentist or periodontist to discuss your concerns, goals, and expectations. This allows the dental professional to evaluate your oral health, assess the extent of gum recession, and determine the most appropriate grafting technique for your case.
- Medication and Health History: Provide a comprehensive medical history, including any medications, supplements, or allergies you have. Inform your dentist about any existing health conditions or recent illnesses to ensure they are considered in your treatment plan.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain a consistent and thorough oral hygiene routine leading up to the procedure. Brush your teeth at least twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss daily. Good oral hygiene helps reduce harmful bacteria and contributes to successful healing.
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, it is highly recommended to quit or abstain from smoking for a significant period before and after the surgery. Smoking can impair blood flow, delay healing, and increase the risk of complications.
- Avoid Blood-Thinning Medications: Your dentist may advise you to temporarily stop taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or anticoagulants, before the procedure to minimize bleeding during and after surgery. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
- Fasting: Depending on the type of anesthesia used during the procedure, your dentist may instruct you to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period before the surgery. Follow these fasting instructions carefully to prevent any complications.
- Transportation and Accompaniment: Make arrangements for someone to drive you to and from the dental office, especially if you are under sedation or have extensive procedures. Having a responsible adult accompany you can provide support and assistance during your recovery.
- Comfortable Attire: Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of the surgery to ensure ease of movement and to accommodate any postoperative dressings or bandages.
- Postoperative Supplies: Purchase any recommended postoperative supplies, such as pain medication, mouth rinse, gauze, and ice packs, before the procedure. This way, you will have them readily available for your recovery period.
Remember to follow your dentist’s instructions and guidelines to ensure optimal preparation for gingival grafting. Clear communication and compliance with preoperative guidelines promote a smooth surgical experience and successful healing.
What to Expect During the Gingival Grafting Procedure
Several key steps and elements can be expected during the gingival grafting procedure. While specific details may vary depending on the technique used and individual circumstances, here is a general overview of what to expect during a gingival grafting process:
- Anesthesia: Before the procedure begins, the dental professional will administer a local anesthetic to numb the treated area. This ensures a comfortable and pain-free experience during the surgery.
- Graft Harvesting: There are different graft sources, including the patient’s own tissue (autograft), donor tissue (allograft), or synthetic materials. If an autograft is used, a small section of tissue is typically harvested from the palate (roof of the mouth) or another donor site. The area is carefully prepared and sutured afterward.
- Graft Placement: The harvested or selected graft material is then carefully positioned over the exposed root surfaces or areas of gum recession. The graft is secured in place using sutures or other fixation techniques.
- Incision Closure: If necessary, any additional incisions made during the procedure are closed using sutures. These sutures may be dissolvable or require removal at a follow-up appointment.
- Postoperative Care Instructions: Following the procedure, the dental professional will provide detailed postoperative care instructions. These instructions may include guidelines for pain management, oral hygiene, dietary restrictions, and any specific precautions to take during the healing process.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Depending on the case, follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the healing progress, remove sutures if needed, and assess the overall success of the grafting procedure.
It is important to note that gingival grafting procedures can vary in complexity and duration based on individual needs and the extent of gum recession. Your dental professional will guide you through the process, explain the specific details of your procedure, and address any questions or concerns you may have.
During the gingival grafting procedure, our dental team will prioritize your comfort and well-being, ensuring a safe and effective treatment to promote gum tissue regeneration, protect exposed roots, and improve oral health.
Postoperative Care and Maintenance
After undergoing gingival grafting, proper postoperative care and maintenance are essential for successful healing and optimal results. Here are some crucial guidelines to follow:
- Take prescribed medication: Your dentist may prescribe pain medication or antibiotics to manage discomfort and prevent infection. Take them as directed.
- Apply ice packs: Applying ice packs to the treated area can help reduce swelling and discomfort. Use them intermittently for the first 24-48 hours.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Maintain oral hygiene by gently brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Be cautious around the surgical site to avoid disturbing the graft. Use an antimicrobial mouth rinse as recommended by your dentist.
- Avoid irritating the graft: Avoid touching, probing, or pulling at the graft area with your fingers, tongue, or toothbrush. Refrain from consuming hot or spicy foods, which can irritate the surgical site.
- Follow a soft diet: Stick to a soft diet for the initial days after surgery. Choose foods that are easy to chew and won’t put excessive pressure on the graft.
- Limit physical activity: Avoid physical activity for a few days after the procedure to prevent excessive bleeding and swelling. Avoid strenuous exercise or actions that may compromise the healing process.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your dentist or periodontist. They will monitor the healing progress, remove sutures if necessary, and provide further instructions.
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, it’s strongly advised to quit or at least abstain from smoking during the healing process. Smoking can impede healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Practice patience: Healing times vary for each individual, but it typically takes a few weeks for the graft to integrate fully and for the gums to stabilize. Be patient and allow your body time to heal.
By adhering to these postoperative care instructions, you can promote proper healing, minimize complications, and enhance the long-term success of your gingival grafting procedure. For personalized advice and guidance, consult your dental professional.
Healing and Recovery after Gingival Grafting
The healing and recovery process for gingival grafting is crucial in achieving successful outcomes. Understanding what to expect during this period can help you navigate it effectively. Here is an overview of the healing and recovery process:
- Initial Phase (First Few Days):
- Discomfort and Swelling: You may experience mild to moderate discomfort, swelling, and sensitivity in the treated area. This is normal and can be managed with prescribed pain medication or over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Bleeding: Some minor bleeding or oozing from the surgical site may occur initially. Applying gentle pressure with sterile gauze can help control it.
- Rest and Recovery: Take it easy for the first few days after surgery, avoiding strenuous activities that can disrupt the healing process.
- Oral Hygiene: Follow your dentist’s instructions regarding oral hygiene practices. Gently brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush, being careful around the surgical site. Use an antimicrobial mouth rinse if recommended.
- Subsequent Weeks:
- Healing of Incisions: The incisions made during the surgery will start to heal. It is normal to notice scabbing or small white patches as the tissue regenerates.
- Resolution of Swelling: Swelling should gradually subside during this period. Applying ice packs during the initial days can help reduce swelling.
- Suture Removal: If sutures were used, your dentist will schedule a follow-up appointment to remove them, typically within one to two weeks.
- Gradual Gum Tissue Integration: The grafted gum tissue will gradually integrate with the existing gum tissue, improving coverage and stability.
- Long-Term Healing:
- Complete Integration: Over several weeks to months, the grafted tissue will fully integrate with the surrounding gum tissue, providing increased thickness and coverage.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with your dentist will allow them to monitor the healing progress, address any concerns, and provide further guidance for long-term care.
- Maintaining Oral Hygiene: Good oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and routine dental cleanings, are vital for the long-term success of the grafting procedure.
- Lifestyle Factors: Avoid habits that can hinder healing, such as smoking or consuming alcohol excessively, as they can compromise the graft’s success.
It’s important to note that the healing process can vary among individuals, and it may take several months to appreciate the final results fully. Following your dentist’s postoperative instructions, attending follow-up appointments, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle will contribute to successful healing and long-term oral health. If you experience severe or prolonged discomfort, excessive bleeding, or other concerning symptoms, contact us at (877) 440-3564 for evaluation and guidance.
Long-Term Care and Maintenance after Gingival Grafting
Long-term care and maintenance after gingival grafting are crucial to preserve the procedure results and ensure optimal oral health. Here are some essential tips to follow:
- Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Gently clean around the graft area, being careful not to apply excessive pressure. Floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria from between teeth.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor the health of your gums and overall oral condition. Your dentist will assess the graft site, perform professional cleanings, and provide personalized advice for maintenance.
- Use a Non-Alcoholic Mouth Rinse: Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial, non-alcoholic mouthwash as your dentist recommends. This helps reduce bacteria and promotes a healthy oral environment.
- Avoid Tobacco and Smoking: Smoking and tobacco use can compromise healing and increase graft failure risk. Quitting smoking is crucial for long-term oral health and the success of the graft.
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health and overall healing. Limit sugary foods and beverages that can contribute to plaque formation and gum disease.
- Manage Teeth Grinding: Discuss with your dentist if you grind or clench your teeth, known as bruxism. They may recommend a nightguard or other appliances to protect the graft and prevent further gum recession.
- Address Dental Issues Promptly: Seek immediate dental care if you notice any signs of gum inflammation, gum recession, or changes in the appearance or sensitivity of the graft area. Early intervention can help prevent complications and maintain the integrity of the graft.
- Follow the Dentist’s Recommendations: Your dentist will provide specific instructions tailored to your case. Follow their guidance regarding postoperative care, oral hygiene products, and any additional treatments or procedures that may be necessary.
By following these long-term care guidelines and maintaining a proactive approach to oral health, you can preserve the results of your gingival grafting procedure and enjoy a healthy, attractive smile for years. Regular communication with your dental professional addresses concerns and ensures ongoing success.
Clinical Outcomes and Efficacy of Gingival Grafting
Gingival grafting has demonstrated favorable clinical outcomes and proven efficacy in addressing gum recession and improving oral health. Numerous studies and clinical observations support its effectiveness in various aspects. Here are some key findings regarding the clinical outcomes and efficacy of gingival grafting:
- Root Coverage: Gingival grafting procedures, such as free gingival grafts and connective tissue grafts, have shown high rates of successful root coverage. These grafts effectively restore gum tissue, reducing or eliminating the exposed root surface and enhancing the smile’s aesthetics.
- Reduction in Tooth Sensitivity: Gingival recession often increases tooth sensitivity, particularly temperature changes and certain foods or drinks. Gingival grafting procedures cover the exposed root surfaces, significantly reducing tooth sensitivity and improving patient comfort.
- Preservation of Tooth Stability: Gum recession can contribute to tooth mobility and potential tooth loss if left untreated. Gingival grafting helps stabilize the affected teeth by re-establishing a healthy attachment of gum tissue, reducing the risk of further gum recession and associated complications.
- Improved Oral Health: Gingival grafting aids in the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases by restoring gum tissue and eliminating pockets that harbor bacteria. It facilitates better oral hygiene practices, enhances plaque control, and reduces the risk of inflammation and gum infection.
- Long-Term Stability: Long-term studies have shown that gingival grafting procedures provide stable and sustainable results. The transplanted gum tissue integrates with the existing tissue, maintaining its position and functionality over time.
- Patient Satisfaction: Gingival grafting procedures have consistently shown high levels of patient satisfaction. Patients report improved aesthetics, reduced tooth sensitivity, enhanced oral comfort, and increased confidence in their smiles.
It is important to note that the success and efficacy of gingival grafting can vary depending on factors such as the severity of gum recession, patient compliance with postoperative care, and individual healing capabilities. A thorough evaluation by a dental professional is crucial to determine the most appropriate grafting technique and ensure optimal outcomes.
Overall, gingival grafting has proven to be an effective and reliable treatment option for addressing gum recession, improving oral health, and enhancing the smile’s aesthetics. Consultation with a qualified dental professional is recommended to assess individual needs and determine the suitability of gingival grafting for each patient.
Clinical Indicators of Successful Gingival Grafting
Successful gingival grafting can be assessed based on several clinical indicators demonstrating the procedure’s effectiveness in addressing gum recession and improving oral health. One of the primary indicators is root coverage, where the graft successfully covers the exposed root surfaces, reducing sensitivity and preventing further root exposure. The increase in gingival thickness and width is another critical indicator, as it signifies the graft’s integration with existing gum tissue, leading to improved gum health and stability.
A successful graft also contributes to an aesthetically pleasing outcome, creating a natural-looking gum line that blends seamlessly with the surrounding tissues. Patients’ feedback and satisfaction reflect improved oral comfort and overall well-being. Additionally, the preservation of periodontal health and the reduction of periodontal pocket depths are significant indicators of successful gingival grafting, as the procedure aids in preventing and treating periodontal diseases.
Long-term follow-up appointments are essential for assessing the stability and longevity of the graft, providing dental professionals with a comprehensive evaluation of the procedure’s success and allowing for adjustments if needed. By considering these clinical indicators, dental professionals can ensure the efficacy and favorable outcomes of gingival grafting procedures for their patients.
Impact of Gingival Grafting on Patient Quality of Life
Gingival grafting can significantly impact the patient’s quality of life, especially for those experiencing gum recession and its associated challenges. One of the key improvements is a reduction in tooth sensitivity. Gum recession often leads to exposed root surfaces, causing heightened sensitivity to temperature changes and certain foods. Gingival grafting covers these exposed areas, alleviating discomfort and allowing patients to enjoy a broader range of foods and beverages without sensitivity concerns. This enhanced oral comfort contributes to an overall improvement in the patient’s daily activities and enjoyment of life.
Furthermore, successful gingival grafting can lead to improved aesthetics. Gum recession can cause an uneven gum line and gaps between teeth, affecting the smile’s appearance. Gingival grafting enhances the smile’s aesthetics by restoring gum tissue and achieving better root coverage, boosting the patient’s self-confidence and self-esteem. Patients often report feeling more at ease with their smiles and are more inclined to engage in social interactions and professional settings without worrying about their gum appearance.
Another significant impact of gingival grafting is the preservation of oral health. Gum recession can lead to periodontal diseases and compromised periodontal health. Gingival grafting helps prevent further gum recession, reduces periodontal pocket depths, and provides a protective barrier against harmful bacteria. Improved periodontal health contributes to better oral health and may positively impact systemic health, as there is a known association between oral health and certain systemic conditions.
Moreover, successful gingival grafting can reduce the risk of further tooth loss. Gum recession can lead to tooth mobility and potential tooth loss if left untreated. By stabilizing the affected teeth and preventing additional gum recession, gingival grafting aids in preserving natural teeth and avoiding the need for extensive dental treatments or tooth replacements.
Gingival grafting can significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life by reducing tooth sensitivity, improving aesthetics, preserving oral health, and promoting overall well-being. Patients often experience improved oral comfort, increased self-confidence, and a greater willingness to engage in social and professional activities. For those seeking a long-lasting solution to gum recession, gingival grafting has a positive impact that extends beyond oral health and improves overall quality of life.
Aesthetic and Functional Outcomes of Gingival Grafting
Gingival grafting can result in aesthetic and functional improvements, addressing various concerns related to gum recession. Here are the aesthetic and functional outcomes of gingival grafting:
Aesthetic Outcomes:
- Improved Gum Line: Gingival grafting can create a more even and aesthetically pleasing gum line. By covering exposed root surfaces and increasing gum thickness, the graft helps eliminate irregularities in the gum line, creating a harmonious smile.
- Enhanced Smile Appearance: Gum recession can cause the teeth to appear longer and create gaps between them. Gingival grafting restores the natural length and proportions of the teeth, resulting in a more attractive and youthful smile.
- Natural-Looking Gum Tissue: The grafting procedure ensures that the transplanted gum tissue blends seamlessly with the existing gum tissue. As a result, the outcome appears natural and indistinguishable from the surrounding gums.
- Increased Self-Confidence: Patients often experience a boost in self-confidence following successful gingival grafting. Individuals may feel more comfortable and confident in social and professional settings with an improved smile appearance.
Functional Outcomes:
- Reduced Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed root surfaces due to gum recession can increase tooth sensitivity. Gingival grafting covers these sensitive areas, relieving discomfort and allowing patients to enjoy hot, cold, and sweet foods without sensitivity issues.
- Improved Chewing Comfort: Gum recession can impact how food is chewed, leading to discomfort during eating. After gingival grafting, patients may find chewing more comfortable and enjoyable.
- Enhanced Oral Health: Gum recession can contribute to periodontal problems and compromise oral health. By addressing gum recession, gingival grafting promotes better oral hygiene, reduces the risk of gum disease, and supports overall oral health.
- Tooth Stability: Gum recession can lead to tooth mobility and potential tooth loss. Gingival grafting stabilizes the affected teeth by re-establishing a healthy gum attachment, helping to preserve natural teeth and prevent further complications.
In summary, gingival grafting provides significant aesthetic and functional benefits. It enhances smile aesthetics, boosts self-confidence, and improves tooth sensitivity. Additionally, the procedure promotes better oral health, enhances chewing comfort, and preserves tooth stability. These combined outcomes improve the patient’s quality of life, making gingival grafting a valuable and effective treatment option for addressing gum recession.
Complications and Management in Gingival Grafting
When considering gingival grafting as a treatment option for gum recession, understanding the potential complications and their management is crucial for patients and dental professionals. While gingival grafting is generally safe and effective, complications can occasionally arise during or after the surgery. Common complications may include postoperative pain, swelling, bleeding, infection, graft failure, and gum texture or color changes. However, these complications can be minimized or managed effectively with proper planning, meticulous surgical technique, and diligent postoperative care. Dental professionals carefully assess patients before the procedure to identify risk factors that may increase the likelihood of complications. Additionally, they provide detailed postoperative instructions and closely monitor patients during the healing process to ensure the best possible outcomes and promote successful gingival grafting.
Common Complications of Gingival Grafting
Gingival grafting is a well-established procedure for addressing gum recession, but like any surgical intervention, it can have potential complications. Awareness of these common complications is essential for patients and dental professionals. Some typical complications during or after gingival grafting include postoperative pain, swelling, and bleeding. While these are generally transient and can be managed with appropriate pain medication and proper postoperative care, they are common occurrences.
Infections at the graft site are also possible but can be minimized with strict adherence to sterile surgical techniques and proper oral hygiene following the procedure. Graft failure, where the transplanted tissue does not fully integrate or heals poorly, can occur, although it is relatively uncommon.
Gum texture or color changes might also be observed, but these usually resolve as the graft heals and matures. By understanding these potential complications, patients can make informed decisions, and dental professionals can take the necessary precautions to ensure the best possible outcomes in gingival grafting procedures.
Managing Complications in Gingival Grafting
Managing complications during or after gingival grafting is essential to ensure successful outcomes and patient satisfaction. Here are some effective strategies for handling common complications:
- Postoperative Pain: Dentists may prescribe pain medication or recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to manage postoperative pain. Patients should take these medications as directed and avoid activities that may exacerbate discomfort.
- Swelling and Bleeding: Applying ice packs to the affected area during the first 24-48 hours can help reduce swelling. To control bleeding, gentle pressure with sterile gauze can be applied. Patients should refrain from vigorous rinsing or spitting to minimize bleeding.
- Infection Prevention: To prevent infections, dental professionals adhere to strict sterile surgical techniques during the procedure. Patients are given instructions for oral hygiene and may be prescribed antibiotics if necessary.
- Graft Failure: Graft failure is relatively uncommon, but a revision surgery may be required to address the issue if it occurs. Dentists closely monitor the healing progress and assess the need for additional interventions.
- Changes in Gum Texture or Color: Any temporary changes in gum texture or color usually resolve as the graft heals and matures. Patients are encouraged to maintain good oral hygiene practices and attend follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process.
- Patient Education and Communication: Educating patients about potential complications and providing clear postoperative care instructions are vital. Encouraging open communication allows patients to express concerns promptly, enabling early intervention if needed.
- Close Monitoring: Dental professionals closely monitor patients during healing, conducting regular follow-up appointments to assess progress and promptly address complications.
By adopting these strategies, dental professionals can effectively manage complications and optimize the success of gingival grafting procedures. Patients play an active role by adhering to postoperative care instructions and promptly reporting issues to their dental providers, contributing to a positive and smooth recovery experience.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Complications in Gingival Grafting
Understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive measures are vital in gingival grafting to ensure successful outcomes and minimize complications. Several factors can increase the risk of complications during and after the procedure. Patients with existing gum disease (periodontitis) are more susceptible to complications, as compromised gum tissue may impede proper healing. Smoking is another significant risk factor that hinders blood circulation and recovery, leading to higher graft failure rates. Poor oral hygiene can contribute to postoperative infections and graft failure, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene before and after the procedure. Additionally, certain systemic health conditions and medications, such as blood thinners, can elevate the risk of bleeding and other complications.
To prevent complications in gingival grafting, a comprehensive approach is essential. Before the procedure, preoperative assessment is crucial to identify risk factors and address underlying oral health issues, such as gum disease. Patient education is vital, as it empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery by adhering to postoperative care instructions and recognizing potential risks. Encouraging smoking cessation before and during the healing process significantly reduces the risk of complications and improves graft success. Collaboration with the patient’s healthcare provider to adjust medications, if necessary, and prescribe antibiotics as prophylaxis for high-risk cases can further minimize complications. Utilizing skilled and experienced dental professionals to perform the grafting procedure ensures precision and reduces the likelihood of complications.
Recognizing and addressing risk factors while implementing preventive measures are vital in mitigating complications during gingival grafting. By taking proactive steps and involving patients in their care, dental professionals can enhance the overall success of gingival grafting procedures and promote optimal patient outcomes. For more information about gingival grafting, call (877) 440-3564 and consult with one of our skilled Periodontists.
Advancements and Future of Gingival Grafting
Advancements in gingival grafting have significantly improved the treatment of gum recession and hold promising potential for the future. In recent years, innovative techniques and materials have emerged, enhancing the efficacy and outcomes of gingival grafting procedures. One notable advancement is using acellular dermal matrix grafts, eliminating donor-site surgery and expediting healing. Additionally, the development of growth factors and tissue engineering technologies has shown promise in promoting faster tissue regeneration and improving graft integration.
Laser-assisted gingival grafting is another groundbreaking advancement that offers minimally invasive procedures, reduced bleeding, and faster healing times. This cutting-edge technique provides patients with enhanced comfort and convenience during recovery.
Moreover, ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore new biomaterials, scaffold designs, and cell-based therapies to optimize gingival grafting outcomes further. These innovations aim to enhance the predictability and success of the procedure while reducing patient discomfort and healing time.
As regenerative medicine advances, the future of gingival grafting holds tremendous potential for personalized treatments tailored to each patient’s unique needs. Customized grafts and biological agents may revolutionize the field, providing long-lasting and natural-looking results.
Emerging Techniques and Technologies in Gingival Grafting
Emerging techniques and technologies in gingival grafting are revolutionizing the treatment of gum recession, offering more efficient, minimally invasive, and patient-friendly approaches. One notable advancement is using acellular dermal matrix grafts, eliminating the need for traditional donor site surgery and reducing patient discomfort and healing time. These grafts provide an off-the-shelf option that promotes rapid tissue integration and regeneration.
Laser-assisted gingival grafting is gaining popularity as a cutting-edge technique that offers precise and minimally invasive procedures. Lasers provide excellent control during surgery, reducing bleeding and promoting faster healing. Patients experience reduced postoperative discomfort and quicker recovery times with this innovative technology.
Furthermore, developing growth factors and tissue engineering has shown great promise in improving graft success rates. Bioactive agents stimulate tissue regeneration and enhance the body’s natural healing processes. This approach promotes faster and more predictable graft integration.
In the future, advancements in 3D printing technology may enable the creation of patient-specific grafts tailored to each individual’s unique anatomy. This personalized approach can enhance grafting outcomes and patient satisfaction significantly.
Additionally, stem cells and biological agents are being explored to enhance tissue regeneration further and improve graft survival. These groundbreaking therapies may revolutionize the field of gingival grafting, offering long-lasting and natural-looking results.
Overall, emerging techniques and technologies in gingival grafting hold immense promise for the future of periodontal therapy. As research and innovation progress, patients can expect more efficient, effective, and personalized treatment options for gum recession, improving oral health, aesthetics, and overall quality of life. Dental professionals should stay updated on these advancements to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Role of Regenerative Medicine in Gingival Grafting
The role of regenerative medicine in gingival grafting transforms the landscape of periodontal therapy, offering innovative approaches to address gum recession and enhance tissue regeneration. Regenerative medicine harnesses the body’s natural healing abilities to promote tissue repair and regeneration. In gingival grafting, regenerative techniques aim to restore gum tissue and stimulate new tissue growth for more predictable and long-lasting outcomes.
One significant application of regenerative medicine in gingival grafting involves growth factors and bioactive agents. These substances are introduced into the grafting site to stimulate the body’s cellular responses, encouraging the growth of new blood vessels and supporting tissue regeneration. By enhancing the body’s natural healing processes, these regenerative agents promote faster graft integration and improved tissue quality.
Another cutting-edge approach in regenerative medicine is the use of tissue engineering technologies. Scientists are developing advanced scaffold designs and biomaterials that act as a framework to support the growth and organization of cells, aiding in regenerating damaged or lost tissue. Tissue-engineered grafts have the potential to provide a more precise and tailored solution for each patient, enhancing the overall success of the gingival grafting procedure.
Stem cell therapy is also a promising avenue in regenerative medicine for gingival grafting. Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, including those needed for gum tissue regeneration. Researchers are investigating the potential of using stem cells to accelerate healing and improve graft outcomes.
The role of regenerative medicine in gingival grafting goes beyond restoring aesthetics. It focuses on restoring the natural function and health of the gums, ultimately leading to improved oral health and overall patient well-being. As research and technology in regenerative medicine continue to advance, gingival grafting is poised to witness even more remarkable innovations, paving the way for better treatment options and further elevating the standards of periodontal care. Dental professionals can play a crucial role by staying updated on these advancements and integrating regenerative techniques into their practice to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Advancements in Graft Materials and Suturing Techniques
Advancements in graft materials and suturing techniques have significantly improved gingival grafting procedures’ outcomes and success rates. Dental professionals now have access to diverse graft materials and innovative suturing methods, allowing for more tailored and effective treatments. Some notable advancements include:
- Acellular Dermal Matrix (ADM) Grafts: ADM grafts are derived from human or animal tissues, with cellular components removed to minimize immune responses. These grafts offer excellent handling characteristics and can be used in subepithelial and free gingival grafting procedures. ADM grafts eliminate the need for harvesting tissue from the patient’s palate, reducing postoperative discomfort and enhancing patient satisfaction.
- Allografts and Xenografts: Allografts are derived from human donors, while xenografts are sourced from animal tissues. These graft materials are scaffold structures to promote the body’s natural regeneration process. They offer high biocompatibility and can be used as an alternative to autografts, simplifying the grafting procedure.
- Growth Factors and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): Using growth factors and PRF has become increasingly popular in gingival grafting. These substances are rich in natural healing elements and help stimulate tissue regeneration, accelerate wound healing, and improve graft integration.
- Advanced Suturing Techniques: Introducing finer sutures and advanced suturing techniques has improved wound closure and reduced postoperative complications. Techniques like the horizontal mattress and sling sutures provide better stability and minimize tension on the graft site.
- Tissue Engineering and 3D Printing: Tissue engineering technologies and 3D printing are revolutionizing graft materials. Researchers are exploring using bioactive scaffolds and patient-specific grafts to enhance tissue regeneration and optimize grafting outcomes.
- Minimally Invasive Approaches: Advancements in graft materials and suturing techniques have allowed for minimally invasive procedures, reducing patient discomfort and promoting faster healing. Laser-assisted gingival grafting is one such approach that offers precise tissue manipulation and minimal bleeding.
These advancements in graft materials and suturing techniques empower dental professionals to choose the most suitable option for each patient, considering the extent of recession, patient preferences, and overall treatment goals. By staying updated on these innovations and integrating them into practice, dental professionals can provide patients with more effective, efficient, and comfortable gingival grafting experiences, improving oral health and aesthetics.
Future Research Directions in Gingival Grafting
The future of gingival grafting is promising, with ongoing research focusing on advancing the field to achieve even better outcomes and patient experiences. Several key research directions are being explored:
- Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering: Researchers continually investigate new biomaterials and tissue engineering approaches to develop more effective graft materials. The aim is to create biocompatible scaffolds that support natural tissue regeneration, reducing the need for autografts and improving the predictability of graft outcomes.
- Growth Factors and Biologics: Future research will likely focus on optimizing growth factors, platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and other biologic agents to enhance tissue healing and integration. Understanding these agents’ optimal dosage and delivery methods will improve their effectiveness in promoting tissue regeneration.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell research holds tremendous potential in gingival grafting. Investigating the role of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerating gum tissue may lead to innovative approaches that accelerate healing and improve graft success rates.
- 3D Printing and Patient-Specific Grafts: Advancements in 3D printing technology may pave the way for patient-specific grafts tailored to individual anatomy. Customized grafts offer the potential for better integration and enhanced aesthetic outcomes.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Future research may explore further refinements in minimally invasive approaches, such as laser-assisted grafting, to reduce patient discomfort, accelerate healing, and enhance the precision of the procedure.
- Long-Term Graft Stability and Durability: Studies focusing on long-term graft stability and durability will provide valuable insights into the longevity of graft outcomes and aid in optimizing treatment plans for sustained success.
- Immune Response and Graft Integration: Understanding the immune response to graft materials and identifying strategies to enhance graft integration will improve grafting outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
- Digital Imaging and Simulation: Advancements in digital imaging and simulation tools may allow clinicians to better plan and visualize graft procedures, leading to more precise and customized treatment approaches.
Future research directions in gingival grafting can revolutionize the field, making it more patient-centric, minimally invasive, and successful. By exploring these innovative avenues, dental professionals can offer cutting-edge treatment options to patients, improving their oral health and quality of life. Continued collaboration between researchers and clinicians will drive these advancements and ensure seamless integration into clinical practice.
Cost and Coverage Aspects of Gingival Grafting
Understanding the cost and coverage aspects of gingival grafting is essential for patients seeking treatment for gum recession. Gingival grafting is a highly effective procedure for addressing gum recession and improving oral health, but the costs can vary depending on several factors. The total price typically includes the surgeon’s fees, anesthesia, graft materials, and postoperative care. Dental insurance coverage for gingival grafting may also vary, with some plans offering partial or full coverage. In contrast, others may consider it a cosmetic procedure and provide limited or no coverage. Patients must inquire about their insurance coverage and discuss payment options with their dental provider to make informed decisions about the financial aspects of gingival grafting. Additionally, the long-term benefits and improved oral health resulting from successful gingival grafting may outweigh the initial costs, making it a valuable investment in maintaining a healthy smile.
Understanding the Costs Associated with Gingival Grafting
Understanding the costs associated with gingival grafting is essential for patients considering this procedure to address gum recession. The total cost of gingival grafting can vary depending on several factors, including the case’s complexity, the extent of gum recession, the type of graft material used, and the geographical location of the dental practice. The cost typically includes preoperative consultations, surgeon fees, anesthesia, graft materials, and postoperative care. Patients should consult with their dental provider to receive a comprehensive treatment plan and a breakdown of the estimated costs involved in their specific case.
It is important to note that gingival grafting is a valuable investment in oral health and aesthetics. Left untreated, gum recession can lead to tooth sensitivity, periodontal problems, and even tooth loss. Gingival grafting not only addresses these issues but also enhances the appearance of the smile, boosting self-confidence. Patients should weigh the long-term benefits of improved oral health and aesthetics against the initial costs of the procedure.
Furthermore, dental insurance coverage for gingival grafting can vary. Some dental insurance plans may cover a portion or all of the costs, depending on the plan’s coverage policy and the severity of the gum recession. Patients should check with their insurance provider to understand their coverage and any potential out-of-pocket expenses.
For patients concerned about the affordability of gingival grafting, many dental practices offer payment plans or financing options to help manage the costs. Patients can discuss these options with their dental provider to find a payment plan that suits their budget.
Understanding the costs of gingival grafting allows patients to make informed decisions about their oral health and choose the most suitable treatment option. While the initial prices may vary, the long-term benefits of improved oral health and aesthetics make gingival grafting a worthwhile investment in maintaining a healthy and confident smile. Patients should consult with their dental provider to understand the costs and explore any available payment options or insurance coverage to ensure a successful and affordable treatment experience.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Gingival Grafting
Various factors contributing to the procedure’s complexity and extent influence the cost of gingival grafting. Understanding these factors is essential for patients to understand the overall cost. Here are some key factors that can affect the price of gingival grafting:
- Severity of Gum Recession: The extent of gum recession plays a significant role in determining the complexity of the procedure. More severe cases may require larger grafts and additional surgical steps, increasing the overall cost.
- Type of Graft Material: Different graft materials, such as acellular dermal matrix (ADM), allografts, or xenografts, have varying costs. The choice of graft material can impact the overall cost of the procedure.
- Grafting Technique: There are various gingival grafting techniques available, such as free gingival graft, connective tissue graft, and pedicle graft. The complexity and time required for each method can influence the overall cost.
- Dental Professional’s Experience and Expertise: The experience and skill level of the dental professional performing the procedure can also affect the cost. Highly experienced specialists may charge higher fees for their services.
- Geographic Location: The cost of living and standard of dental care in different regions can impact the cost of gingival grafting. Dental practices in urban areas or regions with a higher cost of living may charge more for their services.
- Anesthesia and Facility Fees: Using anesthesia during the procedure and the facilities utilized for the surgery can add to the overall cost.
- Preoperative Consultations and Postoperative Care: The number of required preoperative consultations and postoperative care visits can also influence the total cost.
- Dental Insurance Coverage: Dental insurance coverage can vary significantly, with some plans offering partial or full coverage for gingival grafting. In contrast, others may provide limited coverage or consider it a cosmetic procedure with no coverage.
- Additional Treatments: The overall cost may increase if additional dental treatments are required with gingival grafting, such as root planning or other periodontal procedures.
Patients should have a detailed discussion with their dental provider to understand how these factors may impact the cost of their specific gingival grafting procedure. Dental providers can provide a comprehensive treatment plan and estimate the costs involved, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their oral health care. Additionally, exploring payment plans or financing options may help manage the costs for patients concerned about the affordability of the procedure.
Insurance Coverage for Gingival Grafting
Insurance coverage for gingival grafting can vary depending on the dental insurance plan and the patient’s specific circumstances. Generally, dental insurance plans fall into two categories: basic dental plans and comprehensive dental plans.
- Basic Dental Plans: Basic dental plans typically cover preventive and routine dental care, such as regular check-ups, cleanings, and X-rays. Gingival grafting is often considered a specialized and more complex procedure, and basic plans may provide limited or no coverage for such treatments. In some cases, basic plans may cover a portion of the cost of gingival grafting if it is deemed medically necessary, such as for severe gum recession that affects the patient’s oral health.
- Comprehensive Dental Plans: Comprehensive dental plans typically offer more extensive coverage, including major dental procedures like gingival grafting. However, coverage levels can still vary widely, and patients may be responsible for a percentage of the total cost as a co-payment or deductible.
In both cases, patients should check with their dental insurance provider to understand the specifics of their coverage. It is essential to determine whether gingival grafting is considered a covered procedure under their plan and if there are any preauthorization requirements or limitations on coverage.
Patients may explore other payment options for cases where gingival grafting is considered a cosmetic procedure or not covered by dental insurance. Some dental practices offer flexible payment plans or financing options to help manage the cost of the procedure. Additionally, patients can inquire about potential discounts or packages that may make the treatment more affordable.
Before undergoing gingival grafting, patients should discuss their insurance coverage with their dental provider and clearly understand the associated costs. Being informed about insurance coverage and payment options will enable patients to make well-informed decisions about their oral health care and the financial aspects of the procedure.
Navigating Insurance and Financing Options for Gingival Grafting
Navigating insurance and financing options for gingival grafting is crucial for patients considering this procedure to address gum recession. Dental insurance coverage for gingival grafting can vary significantly depending on the plan type and the gum recession’s severity.
While some comprehensive dental plans may provide partial coverage for the procedure, basic plans may offer limited or no coverage. Patients should proactively contact their dental insurance provider to understand the specifics of their coverage, including preauthorization requirements and any out-of-pocket expenses. In cases where gingival grafting is considered a cosmetic procedure or not covered by insurance, patients can explore alternative financing options.
We offer flexible payment plans or financing arrangements, such as CareCredit, to help spread the cost over time. Patients can also inquire about any available discounts or package deals to make the treatment more affordable. Engaging in open communication with our dental providers about insurance coverage and financing options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their oral health care and financial investment in gingival grafting. For more information about our payment plans or financing options, call (877) 440-3564.
FAQ
-
What is gingival grafting?
Gingival grafting is a dental procedure used to treat gum recession. It involves taking tissue from one area of the mouth and grafting it onto the receding gumline to cover exposed tooth roots.
-
Why is gum recession a concern?
Gum recession can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased risk of cavities, and compromised aesthetics. If left untreated, it may also progress to more severe gum and tooth problems.
-
What causes gum recession?
Gum recession can result from various factors, including aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal disease, genetics, hormonal changes, and misaligned teeth.
-
Are there different types of gingival grafts?
There are several types of gingival grafts, including free gingival grafts, connective tissue grafts, pedicle grafts, and acellular dermal matrix grafts. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and the surgeon’s recommendation.
-
Is gingival grafting painful?
Local anesthesia is typically used during gingival grafting to ensure patients are comfortable and do not feel pain during the procedure. Some postoperative discomfort is normal but can be managed with pain medications.
-
How long is the recovery period after gingival grafting?
Recovery times can vary, but most patients can return to their regular activities within a few days to a week. Complete healing may take a few weeks to a few months.
-
Are there risks or complications associated with gingival grafting?
While gingival grafting is generally safe, there can be risks such as infection, graft failure, and postoperative bleeding. These risks are relatively rare and can be minimized with proper care.
-
Will my insurance cover gingival grafting?
Dental insurance coverage for gingival grafting varies by plan. Some comprehensive plans may cover a portion of the procedure, while basic plans may offer limited or no coverage. Check with your insurance provider for details.
-
Can I eat normally after gingival grafting?
Initially, you’ll need to follow a soft diet to avoid placing too much pressure on the graft site. As healing progresses, you can gradually return to your regular diet.
-
How can I maintain my oral health after gingival grafting?
Good oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, are essential for maintaining oral health after gingival grafting. Your dentist will provide specific postoperative care instructions to follow.