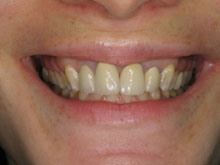
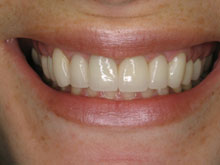
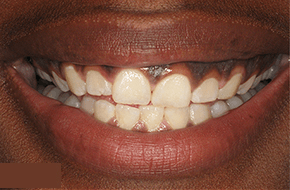
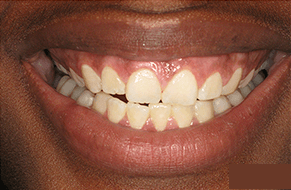
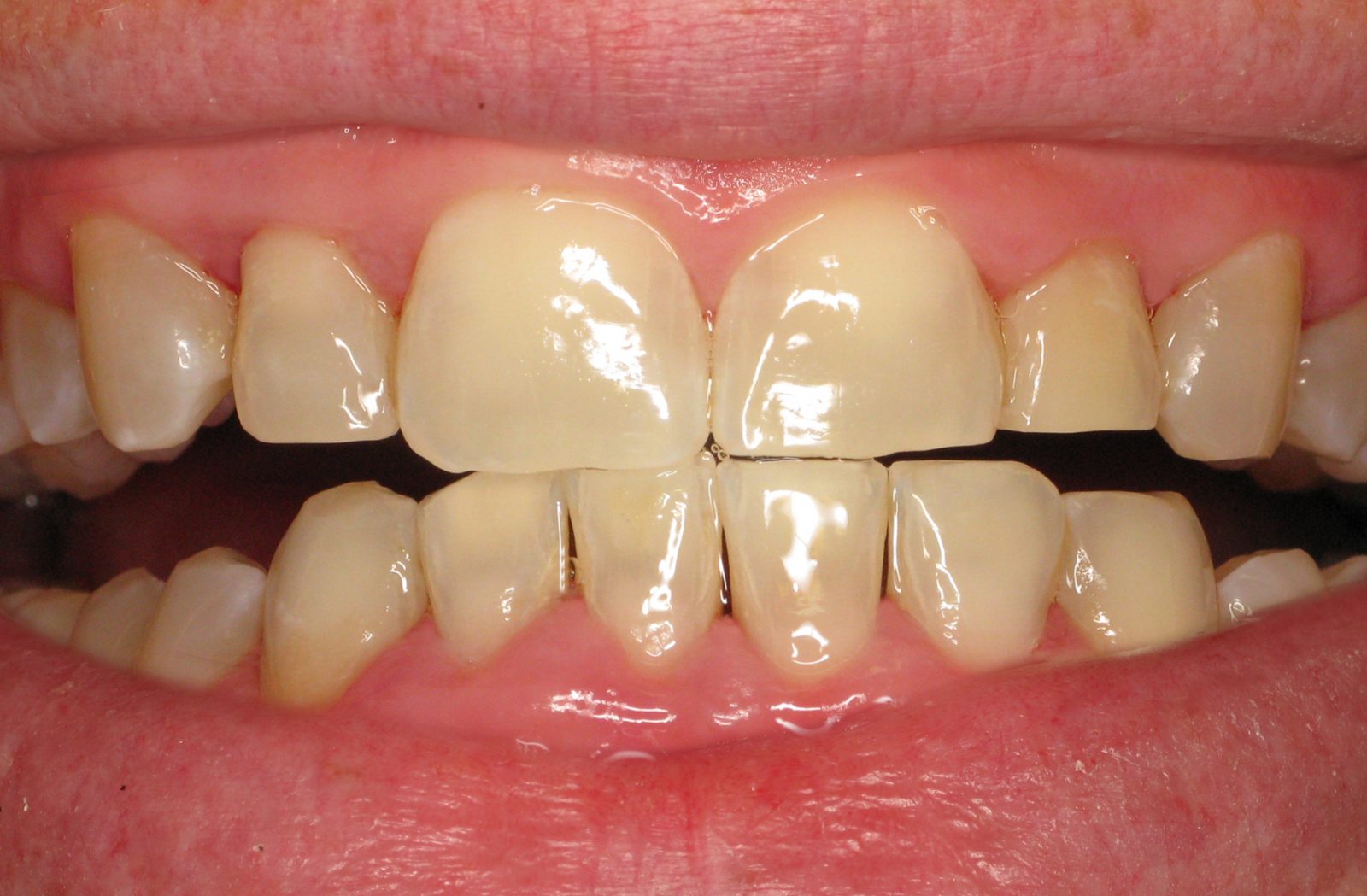
How is Bleeding Gums Diagnosed in Gum Disease?

Diagnosing bleeding gums in gum disease involves a comprehensive assessment by dental professionals to identify the underlying causes and determine an appropriate course of treatment. Our dentists carefully inspect the gums for signs of inflammation, swelling, and bleeding during a dental examination. Probing measurements may be taken to assess the depth of gum pockets, and X-rays or imaging may be employed to evaluate the underlying bone structures.
Our dental professionals consider the patient’s oral hygiene practices, medical history, and potential contributing factors to bleeding gums. The diagnostic process aims to pinpoint the stage of gum disease, identify any systemic factors, and tailor an effective treatment plan. Early detection and diagnosis are critical in preventing gum disease progression and promptly addressing bleeding gums.
What Are The Indicators During a Dental Examination?
Several indicators help dental professionals identify and assess bleeding gums during a dental examination, providing valuable insights into the patient’s oral health. These indicators include:
- Visual Inspection: Dentists visually examine the gums for signs of inflammation, redness, and swelling. Bleeding gums may appear redder than usual, and the presence of blood during the examination is a clear indicator of ongoing issues.
- Gum Probing: Dental professionals use a periodontal probe to measure the depth of the spaces, or pockets, between the teeth and gums. Increased pocket depth and bleeding upon probing may suggest the presence of gum disease.
- Bleeding upon Touch: Gently touching or probing the gums during the examination helps identify areas prone to bleeding. Healthy gums should not bleed upon light pressure, and any bleeding indicates potential gum inflammation or disease.
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s history, including their oral hygiene practices, lifestyle factors, and any systemic conditions, provides context for bleeding gums. Factors such as smoking, medication use, or hormonal changes can contribute to gum bleeding.
- X-rays and Imaging: Radiographic images may be taken to assess the underlying bone structures and identify any bone loss associated with advanced gum disease. These images aid in diagnosing the severity of the condition and planning appropriate interventions.
- Bleeding Index: Dental professionals may use a bleeding index to quantify and record the extent of bleeding during the examination. This index helps track changes in bleeding over time and assess the response to treatment.
- Oral Cancer Screening: In some cases, bleeding gums may be associated with oral lesions or cancers. A thorough examination includes an oral cancer screening to rule out such possibilities.
Identifying these indicators during a dental examination allows for a comprehensive gum health assessment. The presence of bleeding gums is a critical sign of potential gum disease or other underlying issues, prompting further investigation and the development of an appropriate treatment plan. Regular dental check-ups facilitate early detection and intervention, helping preserve optimal oral health and preventing gum-related complications.
How Is The Bleeding Assessed During Brushing or Flossing?
Assessing bleeding during brushing or flossing is crucial to monitoring gum health and identifying potential issues such as gum disease. Dental professionals and individuals can use specific observations and techniques to assess bleeding during these oral hygiene practices:
- Visual Inspection: Observing the appearance of blood on the toothbrush or dental floss during and after brushing or flossing is a direct indicator of bleeding. Any noticeable blood suggests irritation and inflammation of the gums.
- Gum Texture: Feeling the texture of the gums during brushing or flossing can provide insights. Gums that are tender, swollen, or exhibit changes in texture may be more prone to bleeding.
- Color Changes: Healthy gums are typically pink, but inflamed gums may appear redder. Observing color changes during oral hygiene practices can indicate the presence of irritation and bleeding.
- Patient Sensation: Individuals may feel sensitivity or discomfort during brushing or flossing, which can be an additional sign of potential gum issues. Sensations of tenderness or pain can be associated with bleeding gums.
- Gum Bleeding Index: Dental professionals may use a bleeding index to systematically assess and record the extent of bleeding during brushing or flossing. This quantitative measure helps track changes over time and guides the evaluation of the effectiveness of oral care practices.
Assessing bleeding during brushing or flossing is an immediate and tangible indication of potential gum issues. Healthy gums should not bleed during routine oral hygiene activities. The presence of bleeding suggests that the gums may be inflamed, and further investigation is warranted to determine the underlying cause, such as gingivitis or periodontitis.
Addressing bleeding during oral hygiene requires attention to proper technique, consistency in oral care routines, and seeking professional dental advice for a comprehensive assessment and tailored treatment plan. Regular self-assessment, combined with routine dental check-ups, contributes to maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the progression of gum-related complications. If you notice any of these symptoms while brushing or flossing, consult with our Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery dental professionals by calling (877) 440-3564.
Are Specific Tests or Assessments Performed to Confirm Gum Disease?
Specific tests and assessments are conducted during a dental examination to confirm the presence and severity of gum disease. Dental professionals employ various diagnostic tools and techniques tailored to evaluate the extent of gum disease and its impact on oral health.
One key assessment involves using a periodontal probe to measure the depth of gum pockets, helping identify areas with potential inflammation and bleeding. Additionally, X-rays or imaging may be utilized to assess the underlying bone structures and detect any signs of bone loss associated with advanced stages of gum disease. These diagnostic measures provide a comprehensive understanding of the condition, aiding in formulating a personalized treatment plan.
Furthermore, dental professionals may assess bleeding gums as part of a bleeding index, quantifying the extent of bleeding during specific tests and activities, offering valuable insights into the severity of gum disease, and guiding appropriate interventions. Regularly utilizing these diagnostic tools facilitates early detection and enables prompt, targeted management of gum disease for optimal oral health outcomes.