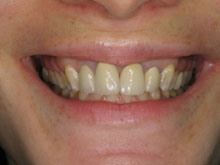
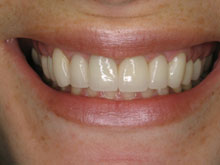
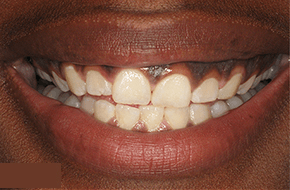
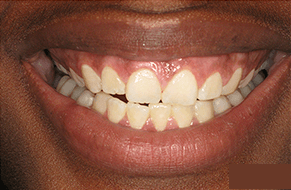
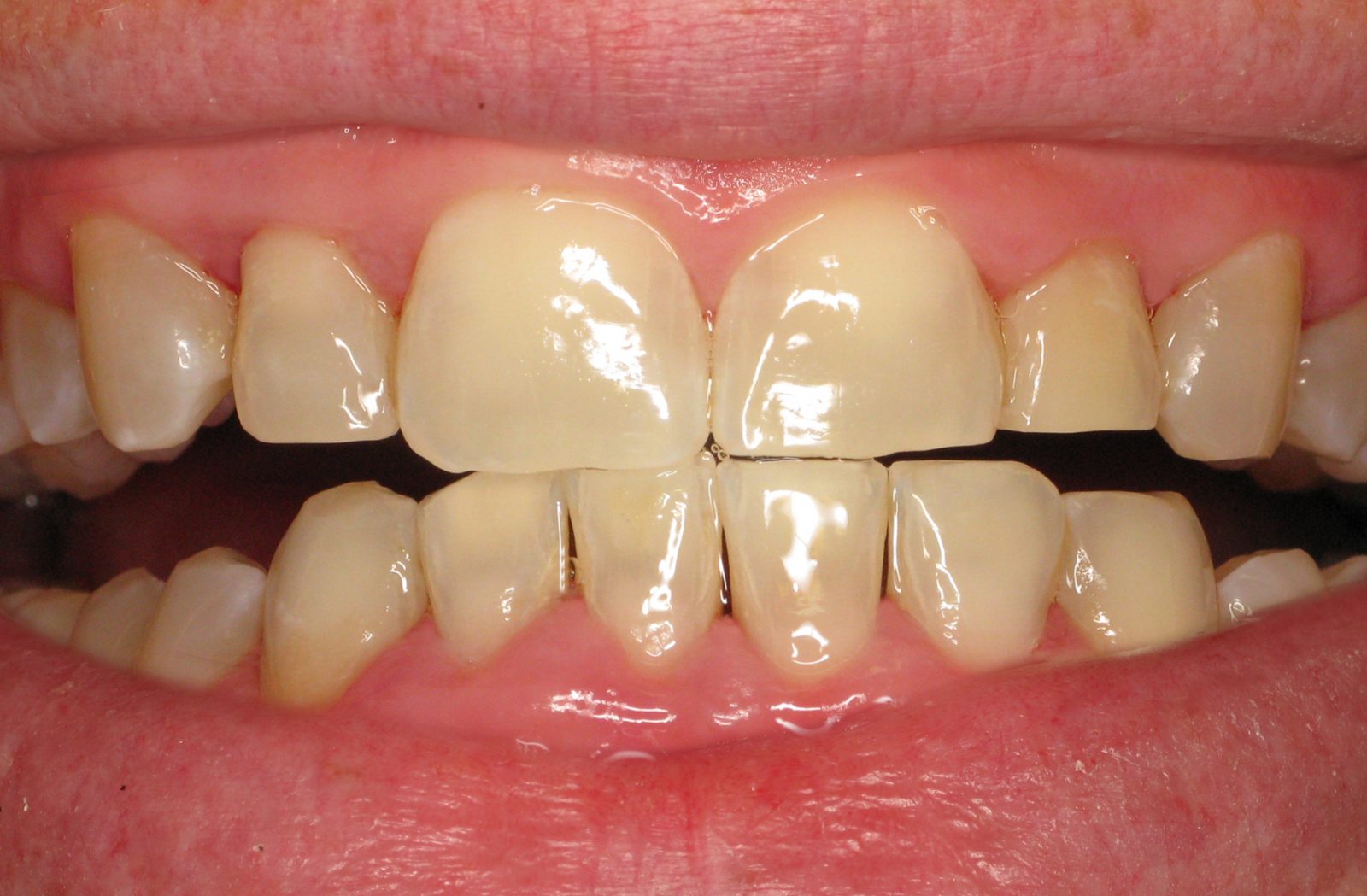
How Is Swelling Diagnosed in Gum Disease?

Diagnosing swelling in gum disease involves a comprehensive dental examination conducted by a dental professional to assess the extent of gum inflammation and identify potential causes. Swelling in gum disease is often diagnosed through visual inspection and careful assessment of the gum tissues. During the examination, our periodontists examine the gums for signs of redness, puffiness, tenderness, and enlargement, which are indicative of gum swelling.
Our dental professionals may also use specialized tools such as periodontal probes to measure gum pocket depths and evaluate the severity of swelling and inflammation. X-rays or other imaging techniques might also be employed to assess bone loss or other underlying issues contributing to gum swelling. Diagnosing gum swelling is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan and interventions needed to manage gum disease effectively. Regular dental check-ups facilitate early detection and timely management of gum swelling, preventing the progression of gum disease and ensuring optimal oral health.
What methods do dentists use to diagnose gum tissue swelling?
At Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery, our dental professionals employ various methods to accurately diagnose gum tissue swelling, a common symptom of gum disease. Our experienced periodontists meticulously assess the gums using specialized techniques during a comprehensive dental examination. Visual inspection is crucial, allowing us to identify signs of swelling, redness, tenderness, and puffiness in the gum tissues. Additionally, we utilize precise periodontal probes to measure gum pocket depths, evaluating the extent of swelling and inflammation.
Advanced imaging technologies, including X-rays or digital imaging, aid in assessing underlying bone structures and identifying any bone loss associated with gum swelling. Our dedicated team combines expertise and innovative diagnostic tools to precisely diagnose gum tissue swelling, enabling us to tailor treatment plans effectively for managing gum disease. Regular visits to our practice facilitate early detection and personalized care, ensuring optimal gum health and preventing the progression of gum swelling and associated complications. To schedule a consultation, call (877) 440-3564.
How is the evaluation of gum texture and size conducted?
Evaluating gum texture and size is essential to a comprehensive dental examination to assess overall gum health. Dental professionals conduct this evaluation through visual inspection and tactile examination, examining various aspects to determine the condition of the gums.
- Visual Inspection: Dentists assess the gums’ color, texture, and appearance. Healthy gums typically appear pink or coral in color and have a firm texture. Any deviation from this, such as redness, swelling, or changes in color, could indicate gum inflammation or disease. Abnormalities in gum size, such as enlarged or receding gums, are also noted during visual inspection.
- Tactile Examination: Dental professionals palpate the gums gently to assess their texture, firmness, and consistency. Healthy gums feel firm and resilient, firmly attached to the teeth without any puffiness or tenderness. Soft, swollen, or excessively firm gums may indicate underlying issues such as inflammation or gum disease.
- Measuring Gum Pocket Depths: Dentists use a periodontal probe to measure the depth of spaces (gum pockets) between the gums and teeth. Deeper pockets often indicate gum disease, as healthy gums typically have shallow pockets.
- Assessment of Gum Recession: Evaluating gum recession involves checking if the gums have receded, exposing the tooth roots. Exposed roots may indicate gum disease or aggressive tooth-brushing habits.
- Digital Imaging and X-rays: In some cases, dental professionals may use digital imaging or X-rays to assess bone levels and detect any bone loss associated with gum disease. These imaging techniques help evaluate the underlying structures supporting the gums and teeth.
A comprehensive evaluation of gum texture and size is crucial for detecting signs of gum disease, gingivitis, or other oral health issues. Regular dental check-ups facilitate early detection, allowing for timely intervention and personalized treatment plans to maintain optimal gum health.
What techniques are used to identify areas of inflammation and swelling?
Dental professionals use various techniques to identify areas of inflammation and swelling in the gums, aiding in diagnosing gum disease and related oral health issues:
- Visual Inspection: Dentists visually examine the gums for signs of inflammation and swelling. Redness, puffiness, and gum texture or size changes are observable indicators of inflammation. These visual cues often guide the initial assessment of potential problem areas.
- Probe Measurements: Periodontal probing involves using a thin dental instrument called a periodontal probe to measure the depth of gum pockets. Deeper pockets typically indicate inflammation and gum disease. Increased pocket depths are indicative of swelling and potential infection.
- Gum Tissue Assessment: Tactile examination allows dental professionals to feel for changes in gum texture, firmness, and consistency. Swollen, tender, or unusually soft gums may signify areas of inflammation.
- X-rays and Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques such as X-rays or digital imaging help identify hidden signs of inflammation, bone loss, or swelling not visible during a regular visual examination. These tools provide a comprehensive view of the underlying bone structures and can aid in diagnosing severe cases of gum disease.
- Bleeding on Probing: Bleeding upon probing or during routine dental cleaning can indicate active inflammation in the gums. Bleeding gums often signal the need for further evaluation and potential treatment.
- Computerized or Laser-Assisted Diagnostic Tools: Some dental practices use advanced technologies like lasers or computerized systems to aid in identifying areas of inflammation and assessing gum health more accurately. These tools can detect subtle changes in the gums that might not be visible to the naked eye.
By combining these techniques, dental professionals can effectively identify areas of inflammation and swelling in the gums. Early detection of these signs allows for prompt intervention and tailored treatment plans to address gum disease, prevent its progression, and maintain optimal oral health. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for monitoring gum health and ensuring timely intervention when signs of inflammation or swelling arise.
How Is Swelling Treated In Gum Disease?
Treating swelling in gum disease involves comprehensive approaches aimed at reducing inflammation, addressing the underlying causes, and restoring optimal gum health. Dental professionals employ various strategies tailored to each patient’s specific condition and severity of gum disease. Treatment typically begins with thorough professional cleanings, such as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria causing the inflammation. This process aims to eliminate irritants and promote healing of the swollen gums.
Additionally, personalized oral hygiene instructions are provided to ensure effective at-home care. Advanced treatments, including laser periodontal therapy, may be recommended to target deep-seated infection and reduce swelling in more severe cases. Managing gum disease often involves a multifaceted approach that emphasizes regular dental visits, maintenance of good oral hygiene practices, and, if necessary, adjunctive treatments to alleviate swelling and restore gum health. Early intervention is crucial in preventing the progression of gum disease and mitigating the effects of swelling on overall oral wellness.
Experienced, professional gum treatment. Offices in New York City, Long Island, Nutley, New Jersey.
Free screening visits will include the following: Oral exam/cancer screening, periodontal evaluation, your possible treatment options, and estimated costs.