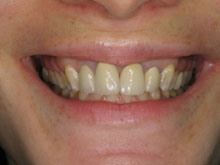
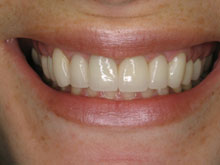
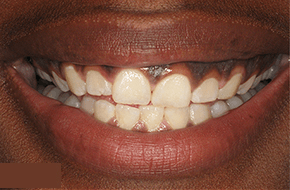
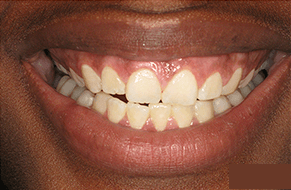
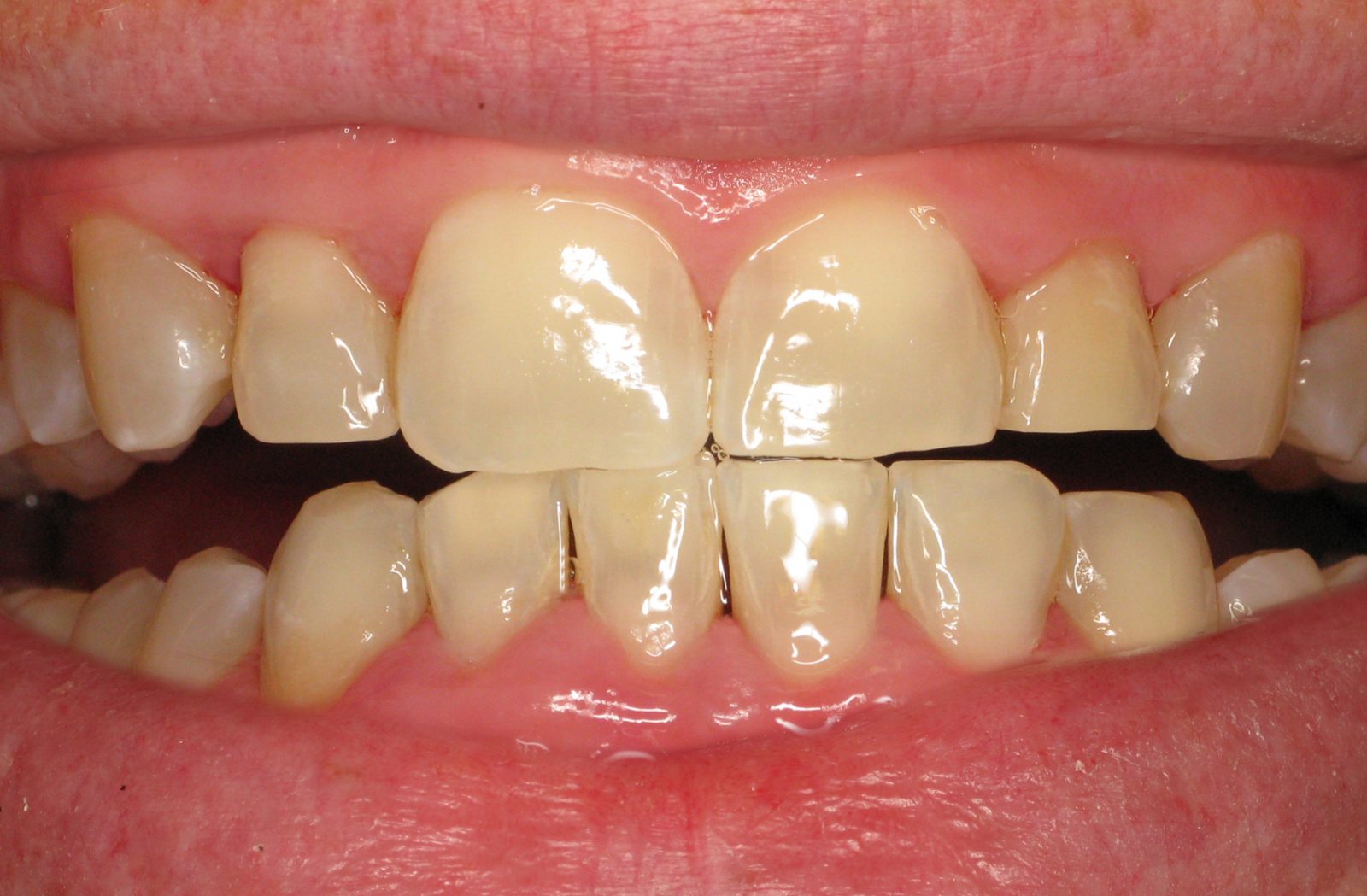
What Are The Potential Risks and Complications Of Bleeding Gums In Gum Disease?

Bleeding gums, often a symptom of gum disease, should not be overlooked, as they can signal underlying issues that, if left untreated, may lead to more serious complications. Persistent gum bleeding may indicate inflammation, infection, or the presence of gum disease. Ignoring these symptoms can contribute to the progression of gum disease, potentially resulting in more severe conditions like periodontitis.
The risks associated with untreated bleeding gums include tooth loss, gum recession, and damage to the supportive structures of the teeth. If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, such as persistent bleeding gums, it is crucial to seek professional dental care promptly.
At Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery, our experienced team specializes in advanced periodontal treatments, including laser therapies, to effectively address gum disease and its associated complications. Contact us for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan to safeguard your oral health.
What Risks Are Associated with Persistent Bleeding Gums?
Persistent bleeding gums, especially when associated with conditions like gum disease, can pose several risks and potential complications. Understanding these risks is essential for prompt intervention and effective management:
- Progression of Gum Disease: Persistent bleeding gums are often an early sign of gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis. Advanced gum disease poses a higher risk of irreversible damage to the gums, teeth, and supporting structures.
- Tooth Loss: Untreated gum disease can form periodontal pockets and spaces between the gums and teeth. As these pockets deepen, the stability of the teeth is compromised, increasing the risk of tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss.
- Gum Recession: Prolonged inflammation and untreated bleeding can contribute to gum recession, where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth. Gum recession exposes the tooth roots, making them more vulnerable to decay and sensitivity.
- Compromised Tooth-Supporting Structures: Persistent bleeding gums can break the ligaments and fibers that anchor the teeth in the jaw. This compromises the integrity of the tooth-supporting structures, leading to increased mobility and the potential for tooth loss.
- Oral Health Complications: Gum disease is linked to systemic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and respiratory problems. The persistent presence of bleeding gums may contribute to these complications if the underlying gum disease is not addressed.
- Chronic Inflammation: Prolonged inflammation in the gums can have systemic effects, impacting overall health. Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory conditions throughout the body.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Bleeding gums can be aesthetically displeasing, affecting the smile’s appearance. Gums’ color and contour changes may become more noticeable as gum disease progresses.
To mitigate these risks, seeking professional dental care at the first signs of persistent bleeding gums is crucial. Dental professionals can provide a comprehensive evaluation, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatments to address gum disease and prevent further complications. Regular dental check-ups, combined with consistent oral hygiene practices, are essential in maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the progression of gum-related issues.
How Might Untreated Bleeding Gums Progress to Advanced Stages?
Untreated bleeding gums can progress to advanced stages of gum disease through a series of interconnected stages, each marked by escalating severity of oral health issues. Here is a detailed explanation of how untreated bleeding gums may advance to more severe stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: The initial stage is often gingivitis, characterized by inflamed and bleeding gums. Gingivitis is primarily caused by plaque accumulation along the gum line, leading to bacterial irritation. Gingivitis may persist and advance if not addressed promptly with professional dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene.
- Periodontal Pockets: As gingivitis progresses, the inflammation can form periodontal pockets—spaces between the gums and teeth. These pockets create a favorable environment for bacteria to thrive, contributing to persistent inflammation and bleeding. Without intervention, the pockets deepen, making it challenging for individuals to clean effectively during routine oral hygiene practices.
- Loss of Connective Tissue: Continued bacterial activity and inflammation compromise the connective tissues that anchor the teeth in the jaw. This leads to the breakdown of the ligaments and fibers supporting the teeth, resulting in increased tooth mobility.
- Bone Loss: Advanced stages of gum disease, known as periodontitis, involve losing supporting bone around the teeth. The chronic inflammatory response triggered by untreated gum disease stimulates the body’s immune system, destroying bone tissue. Progressive bone loss further contributes to tooth instability.
- Tooth Mobility and Shifting: With the weakening of the supporting structures, affected teeth may become mobile or shift out of their normal positions. This not only impacts the alignment of the teeth but also compromises their function and stability.
- Tooth Loss: Ultimately, untreated bleeding gums that progress to advanced stages of gum disease can culminate in tooth loss. The combination of inflammation, bone loss, and compromised tooth-supporting structures can result in irreversible damage, necessitating the extraction of affected teeth.
- Systemic Health Risks: Advanced gum disease is associated with an increased risk of systemic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes complications, and respiratory problems. The chronic inflammation and bacterial dissemination from the oral cavity can contribute to these broader health concerns.
To prevent the progression of gum disease, it is crucial for individuals experiencing bleeding gums to seek timely professional dental care. Dental professionals can provide targeted interventions, including deep cleanings, scaling and root planing, and other periodontal therapies, to address the underlying causes and halt the advancement of gum disease. Consistent oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and prompt intervention at the first signs of bleeding gums are key components of maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the complications associated with advanced gum disease.
Are There Risks Beyond Oral Health, Affecting Overall Well-Being?
The risks of untreated bleeding gums extend beyond oral health, impacting overall well-being and contributing to systemic health concerns. The inflammatory nature of advanced gum disease can lead to a cascade of effects that affect various aspects of an individual’s health:
- Cardiovascular Complications: Chronic inflammation from untreated gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The inflammatory mediators and bacteria associated with gum disease may enter the bloodstream, potentially contributing to the development of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease.
- Diabetes Impact: Individuals with diabetes may experience challenges in managing their blood sugar levels if gum disease is left untreated. Conversely, uncontrolled diabetes can worsen gum disease. This bidirectional relationship emphasizes the importance of oral health in the overall management of chronic conditions.
- Respiratory Issues: The bacteria associated with advanced gum disease can be inhaled into the respiratory tract, potentially contributing to respiratory infections and complications. This is particularly concerning for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
- Compromised Immune Function: Chronic inflammation from untreated gum disease may compromise the immune system’s ability to respond effectively to infections and other health challenges. This can weaken overall immune function, making individuals more susceptible to various illnesses.
- Pregnancy Complications: Pregnant individuals with untreated gum disease may face an increased risk of complications, including preterm birth and low birth weight. The inflammatory response and potential bacterial dissemination can affect maternal and fetal health.
- Joint Problems: Some studies suggest a potential connection between untreated gum disease and certain joint conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic inflammation may contribute to the development or exacerbation of joint problems.
- Cognitive Decline: Emerging research has explored potential links between gum disease and cognitive decline, including conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. While the exact nature of this association is still under investigation, chronic inflammation may affect cognitive function.
- Impact on Overall Quality of Life: Beyond specific health concerns, the discomfort, pain, and aesthetic issues associated with advanced gum disease can significantly impact an individual’s overall quality of life. Chronic oral health problems may affect social interactions, self-esteem, and daily activities.
Addressing bleeding gums and advanced gum disease is crucial for oral health and mitigating the potential systemic consequences. Seeking timely dental intervention, adopting effective oral hygiene practices, and maintaining regular dental check-ups are essential to preserving overall well-being and minimizing the risks associated with untreated gum disease.