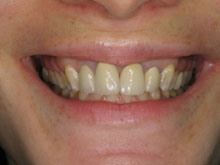
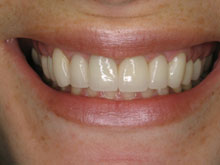
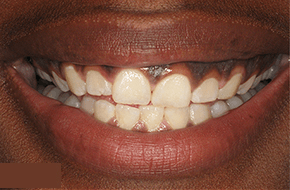
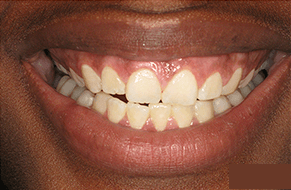
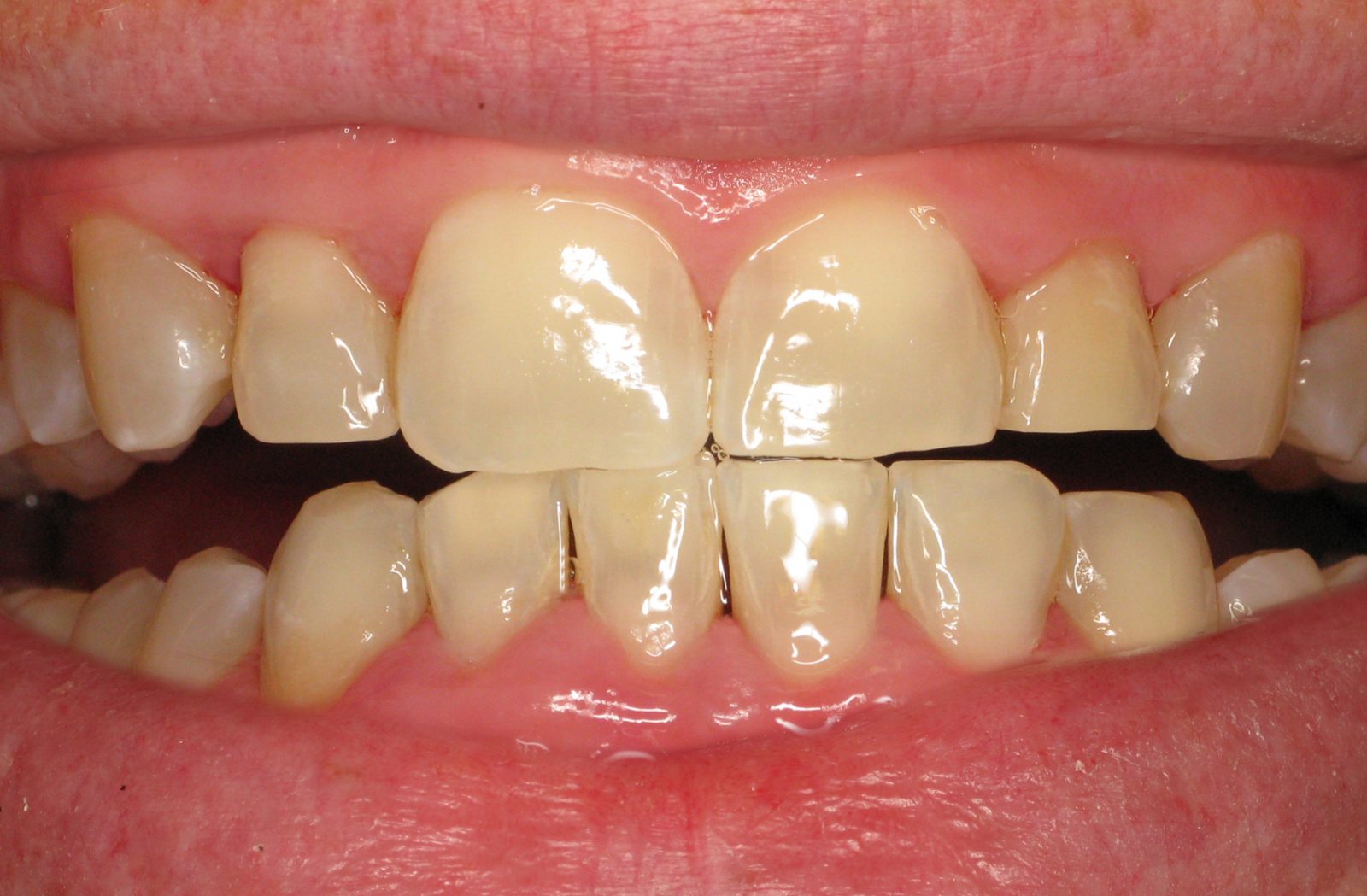
What Are The Potential Risks and Complications of Redness in Gum Disease?

If left untreated, Redness in gum disease can lead to several potential risks and complications affecting oral health and overall well-being. Gum redness is often an early sign of gingivitis or more advanced periodontal conditions, signaling inflammation and possible infection in the gums.
The potential risks and complications associated with gum redness in gum disease include:
- Progression to Periodontitis: Untreated redness in the gums can progress to more severe periodontal disease stages, leading to increased inflammation, gum recession, and potential damage to the supporting bone structures.
- Gum Recession: Persistent redness and inflammation can cause the gums to recede, exposing the tooth roots. Gum recession may lead to increased tooth sensitivity, an unattractive smile, and heightened vulnerability to decay and tooth loss.
- Tooth Loss: Advanced gum disease, characterized by persistent redness and inflammation, can result in tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss due to the destruction of the supportive tissues and bone.
- Systemic Health Concerns: Research suggests a link between gum disease and systemic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes complications, respiratory problems, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Chronic Inflammation: Prolonged gum redness signifies chronic inflammation, which can affect the body’s immune response, potentially contributing to overall systemic inflammation and impacting overall health.
- Compromised Oral Function: As gum disease progresses, redness and inflammation may lead to discomfort, difficulty chewing, and compromised oral function.
Addressing gum redness promptly through professional dental care, such as scaling and root planing, laser periodontal therapy, and personalized oral hygiene, is crucial in preventing the progression of gum disease and minimizing associated risks and complications. Regular dental check-ups and early intervention are essential in managing redness in gum disease, preserving optimal gum health, and reducing the potential risks of untreated gum disease. Seeking professional guidance and maintaining good oral hygiene practices are vital in preventing the escalation of redness in gum disease and maintaining overall oral and systemic health.
How might redness progress to advanced gum disease, known as periodontitis?
If not correctly addressed, redness in the gums can progress to advanced gum disease, also known as periodontitis, through a series of stages characterized by worsening inflammation and tissue damage.
Initially, gum redness may indicate gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis occurs due to plaque accumulation along the gumline, leading to irritation, inflammation, and redness. The gums are inflamed but haven’t yet experienced irreversible damage.
However, when gingivitis remains untreated, the condition can advance to periodontitis. Several factors contribute to this progression:
- Bacterial Accumulation: Persistent plaque buildup along the gumline causes bacterial toxins to trigger an inflammatory response. The body’s immune system responds to fight off the bacteria, leading to ongoing inflammation.
- Gum Tissue Damage: Continuous inflammation damages the gum tissues, causing them to separate from the teeth and creating pockets. These pockets between the gums and teeth become a haven for more plaque and bacteria, exacerbating the condition.
- Loss of Supporting Structures: As periodontitis progresses, the body’s immune response, along with the bacterial infection, can lead to the breakdown of the connective tissues and bone supporting the teeth. This can result in gum recession, tooth mobility, and, in severe cases, tooth loss.
- Increased Severity of Symptoms: Redness and swelling in the gums intensify, and the gums may become more prone to bleeding, tenderness, and pus formation. Additionally, the redness becomes more widespread and pronounced as the disease progresses.
Without intervention, advanced gum disease or periodontitis can cause irreversible damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It significantly increases the risk of tooth loss and may contribute to systemic health issues due to chronic inflammation.
Timely professional intervention, such as scaling and root planing, laser periodontal therapy, and consistent oral hygiene practices, is crucial to halt the progression of redness to advanced gum disease. Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in monitoring gum health and ensuring appropriate treatments to prevent the development of periodontitis and preserve optimal oral well-being. Consult with our experienced Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery dental professionals by calling (877) 440-3564.
What effects can gum bleeding and increased sensitivity have due to gum redness?
Gum bleeding and increased sensitivity resulting from gum redness are common manifestations of gum disease, indicating underlying inflammation and potential damage to the gum tissues. These effects can have several implications for oral health and overall well-being:
- Gum Disease Progression: Gum bleeding, particularly during brushing or flossing, is often an early sign of gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease. Increased sensitivity in the gums can accompany this bleeding, indicating inflammation and irritation of the gum tissues. If left unaddressed, these symptoms may progress to more severe stages of gum disease, such as periodontitis, leading to further gum damage and potential tooth loss.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent gum bleeding and heightened sensitivity indicate chronic inflammation in the gums. Chronic inflammation can contribute to an overactive immune response, potentially affecting systemic health and increasing the risk of various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes complications, and respiratory issues.
- Discomfort and Oral Health Concerns: Increased gum sensitivity can cause pain, making brushing and flossing effectively challenging. This may lead to inadequate oral hygiene, further aggravating gum disease and increasing the risk of bacterial buildup, plaque formation, and gum redness.
- Gum Recession: Gum bleeding and increased sensitivity can precede gum recession, where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth. This exposes the tooth roots, making them more susceptible to decay and increased sensitivity to temperature and touch.
- Psychological Impact: Persistent gum bleeding and heightened sensitivity may cause anxiety or concern about oral health, affecting an individual’s confidence and willingness to maintain regular oral hygiene practices.
Addressing gum bleeding and increased sensitivity due to gum redness requires timely intervention and professional dental care. Effective treatments such as scaling and root planing, laser periodontal therapy, and personalized oral hygiene practices are crucial in managing these symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preserving gum health. Regular dental check-ups help monitor gum health and enable prompt intervention to prevent the progression of gum disease, minimizing the adverse effects of gum bleeding and heightened sensitivity.
Are recurrent infections and prolonged inflammation common complications of gum redness?
Recurrent infections and prolonged inflammation are common complications associated with gum redness, especially gum disease. When the gums appear red and inflamed, it often indicates an inflammatory response triggered by bacteria in plaque and tartar along the gumline.
Here’s how recurrent infections and prolonged inflammation can be common complications of gum redness:
- Recurrent Infections: Redness in the gums typically signifies an ongoing inflammatory process due to bacterial infection. If left untreated, this inflammation can lead to recurrent infections, causing persistent redness, swelling, tenderness, and sometimes pus formation in the gums. The cycle of bacterial growth and immune response can result in multiple episodes of infection, further exacerbating gum disease.
- Prolonged Inflammation: The persistent presence of plaque and inadequate oral hygiene contribute to prolonged inflammation in the gums. Chronic gum redness indicates ongoing irritation and immune response, which can lead to prolonged inflammation in the gum tissues. Prolonged inflammation can damage the gum tissues, lead to gum recession, and contribute to the breakdown of the supporting structures of the teeth.
- Complications of Untreated Gum Disease: Recurrent infections and prolonged inflammation are significant complications of untreated gum disease. As gum disease progresses, the risk of developing more severe forms of periodontal disease increases, potentially leading to extensive damage to the gums, teeth, and underlying bone structures. This may result in tooth mobility, gum recession, and tooth loss.
How does redness in gum disease contribute to the risk of tooth loss?
Redness in gum disease, particularly when accompanied by inflammation and other symptoms, significantly increases the risk of tooth loss due to the progressive nature of gum disease and its impact on the supporting structures of the teeth. Several ways in which gum redness contributes to the risk of tooth loss include:
- Gum Recession: Persistent gum redness and inflammation can lead to gum recession, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth. As a result, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making them more susceptible to decay and damage. Gum recession also compromises the attachment of teeth to the supporting bone, increasing the risk of tooth mobility and eventual loss.
- Periodontal Ligament Damage: Advanced gum disease, characterized by redness, swelling, and inflammation, damages the periodontal ligament—a structure that connects the tooth to the surrounding bone. When this ligament is compromised due to prolonged inflammation, it affects the stability and support of the teeth, contributing to tooth mobility.
- Bone Loss: Chronic gum inflammation and infection associated with gum redness can lead to progressive destruction of the alveolar bone, which supports the teeth. As the bone loss continues, the teeth lose their stable foundation, becoming more susceptible to loosening and eventual loss.
- Tooth Mobility and Loss: Prolonged gum disease weakens the supportive structures around the teeth, including the gums, ligaments, and bone. This can increase tooth mobility, where the affected teeth may shift or loosen. Eventually, severe gum disease can lead to irreversible damage and necessitate the extraction of affected teeth.
- Complications of Untreated Gum Disease: If left untreated, gum disease can progress from gingivitis (redness and inflammation) to advanced stages of periodontitis, significantly increasing the risk of tooth loss. The destruction of the supporting tissues and bone due to persistent inflammation and bacterial infection can ultimately result in tooth loss.
Early intervention is crucial to mitigate the risk of tooth loss associated with gum redness and gum disease. Seeking professional dental care, practicing good oral hygiene, and undergoing necessary treatments, such as scaling and root planing, laser periodontal therapy, and regular dental check-ups, are essential in managing gum redness, preventing disease progression, and preserving teeth and overall oral health—call (877) 440-3564 to schedule an appointment with Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery.
Experienced, professional gum treatment. Offices in New York City, Long Island, Nutley, New Jersey.
Free screening visits will include the following: Oral exam/cancer screening, periodontal evaluation, your possible treatment options, and estimated costs.