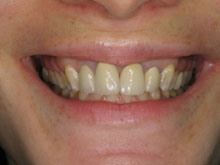
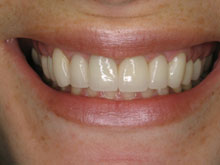
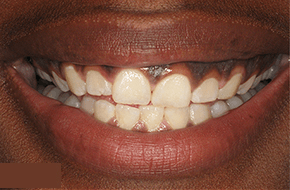
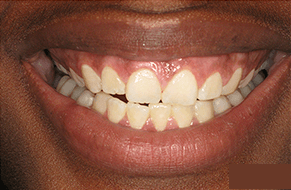
What methods do dentists use to diagnose bad breath associated with gum disease?
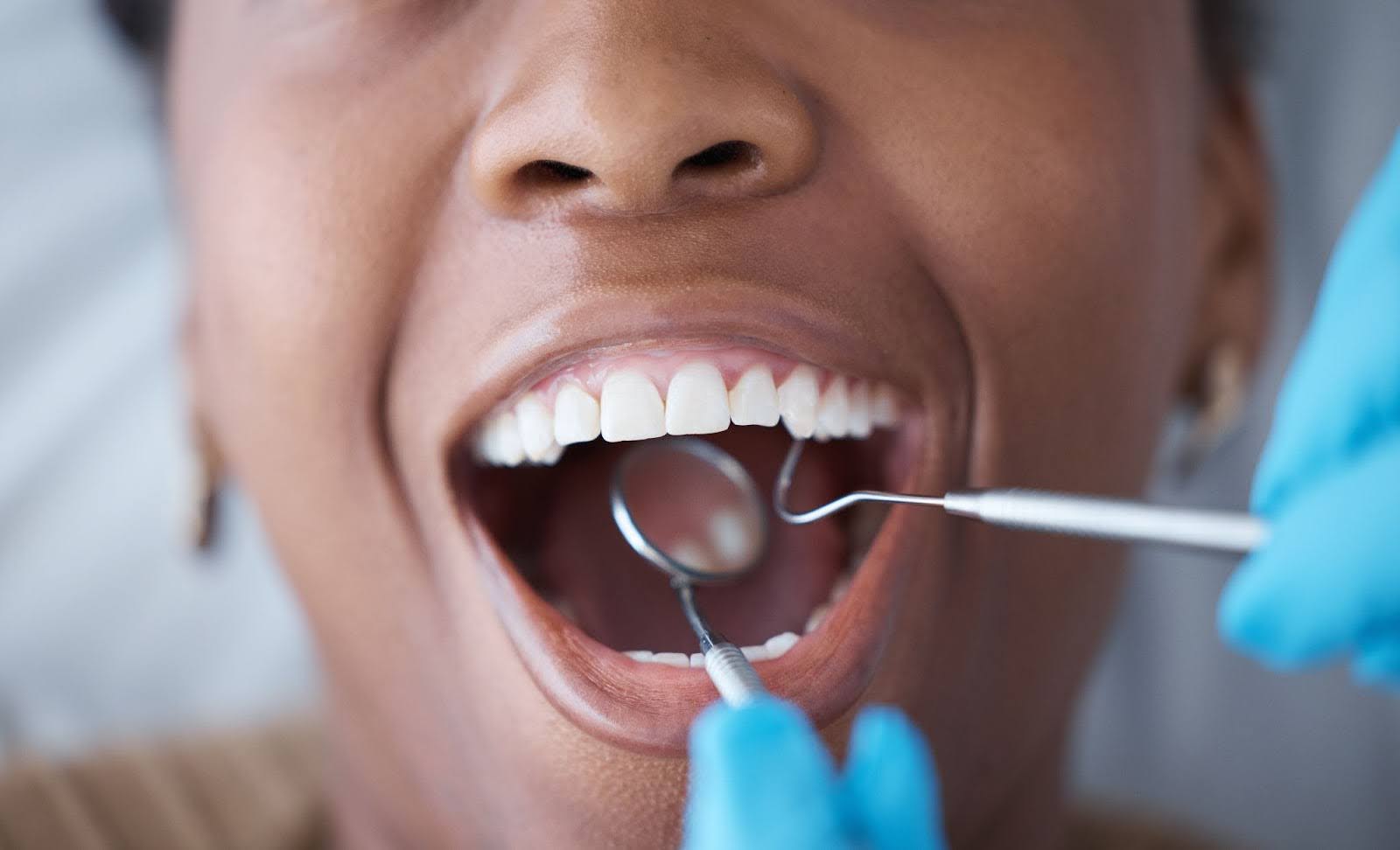
At Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery, our specialists employ advanced methods to diagnose bad breath associated with gum disease with precision and thoroughness.
These diagnostic approaches include:
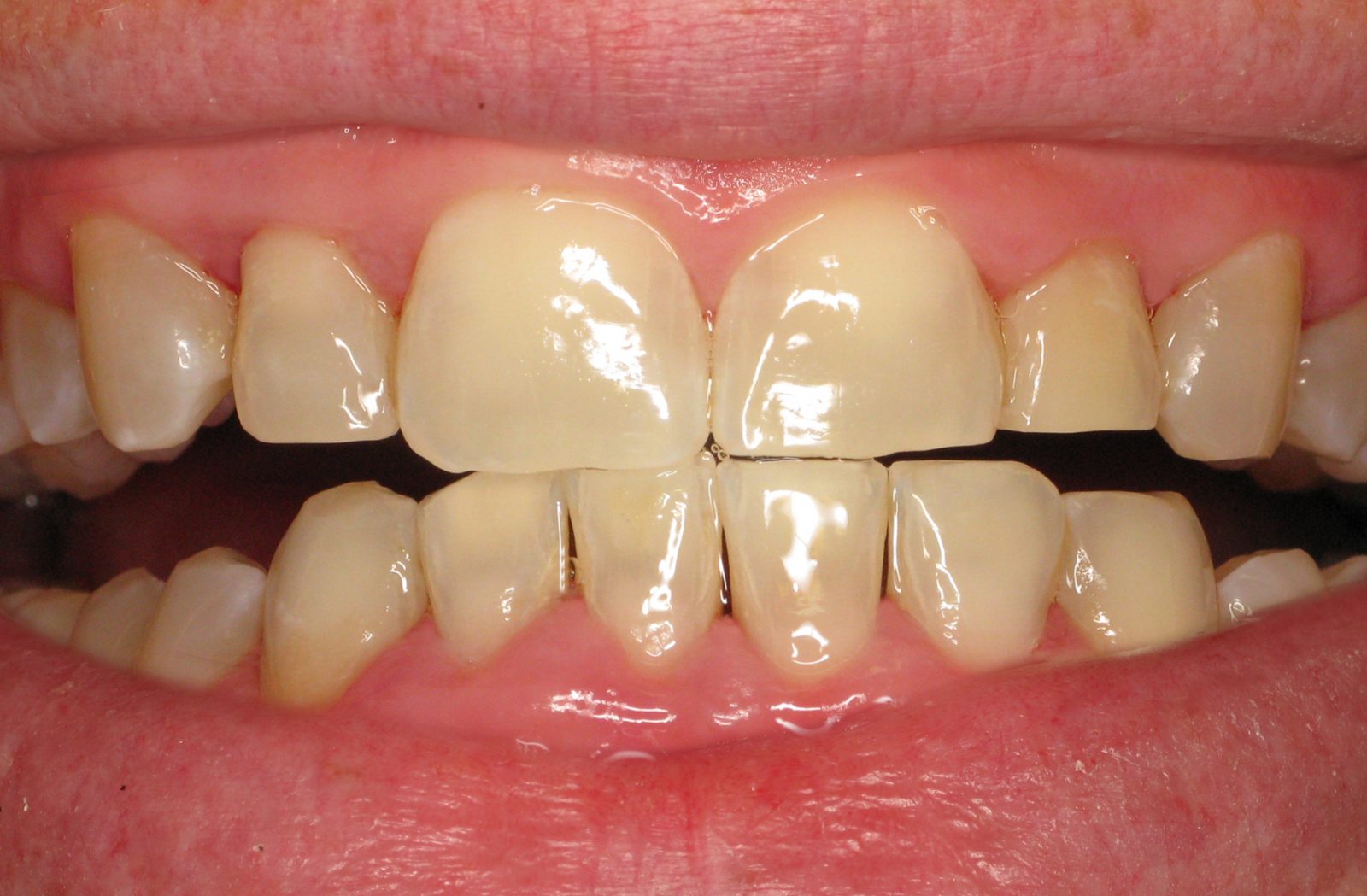
- Comprehensive Oral Examination: Our specialists conduct a detailed examination of the oral cavity, focusing on the health of the gums, teeth, and tongue. This assessment helps identify signs of gum disease, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, and other potential contributors to bad breath.
- Periodontal Probing with Laser Technology: We utilize state-of-the-art laser technology for periodontal probing. This allows for precise measurements of periodontal pocket depths, identifying areas of concern where bacteria may thrive and contribute to bad breath. Laser probing ensures accuracy and minimizes patient discomfort.
- Saliva Analysis: Saliva is crucial in maintaining oral health, and its composition can provide valuable insights. Our specialists may analyze saliva to assess factors such as pH levels, bacteria count, and the presence of compounds that contribute to bad breath.
- Halitosis Assessment: We conduct a specialized halitosis assessment to pinpoint the specific odorous compounds contributing to bad breath. This evaluation helps us understand the nature of the malodor and tailor treatment accordingly.
- Review of Medical History: Understanding a patient’s medical history is vital in diagnosing bad breath. Certain systemic conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors can contribute to oral malodor, and a comprehensive review helps us consider all potential factors.
- Oral Hygiene Evaluation: Our specialists assess an individual’s oral hygiene practices, providing personalized recommendations for improvement. Inadequate oral care can contribute to gum disease and bad breath, making oral hygiene education a crucial aspect of our diagnostic approach.
- Patient Consultation: Open communication with the patient is integral to our diagnostic process. We discuss symptoms, concerns, and any lifestyle factors that may impact oral health. This collaborative approach ensures a thorough understanding of the patient’s experience and aids in formulating a targeted treatment plan.
By combining these diagnostic methods, Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery specialists can accurately identify the underlying causes of bad breath associated with gum disease. This comprehensive approach allows us to tailor effective treatment strategies, utilizing advanced periodontal therapies and laser technologies to address the root causes and provide lasting relief for our patients.
How is the assessment of oral odor conducted during a dental examination?
The assessment of oral odor, also known as halitosis, is a crucial component of a comprehensive dental examination. Dental professionals employ a systematic approach to identify the potential sources and causes of bad breath. Here’s how the assessment of oral odor is typically conducted during a dental examination:
Patient History:
- Symptom Inquiry: Dental professionals begin by asking the patient about their perception of bad breath, including its frequency, duration, and any specific triggers or patterns.
- Medical History: Understanding the patient’s overall health, medications, and any systemic conditions is essential, as certain medical factors can contribute to oral malodor.
External Factors:
- Dietary Habits: Dietary choices, such as consuming strong-smelling foods like garlic or onions, can impact breath odor. Dental professionals inquire about dietary habits to assess their potential influence.
- Lifestyle Habits: Habits like smoking or tobacco use can contribute significantly to bad breath. These factors are considered during the assessment.
Oral Examination:
- Gum Health: The health of the gums is evaluated to identify signs of gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis), a common cause of persistent bad breath. Periodontal probing may be conducted to measure pocket depths and assess the condition of the gums.
- Tongue Examination: The tongue’s surface is examined for coatings, debris, or irregularities. Bacteria can accumulate on the tongue, contributing to bad breath.
- Dental Decay: The presence of dental caries or other dental issues can be a source of malodor. Areas with decay or trapped food particles are identified.
- Oral Appliances: For individuals with dentures, orthodontic appliances, or dental prosthetics, their cleanliness and fit are assessed as these can harbor bacteria contributing to bad breath.
Saliva Analysis:
- Saliva Flow: Reduced saliva flow can lead to dry mouth, increasing the risk of bad breath. Saliva analysis may be conducted to assess saliva quantity and quality.
Halitometer or Breath Testing:
- Instrumental Measurement: Some dental offices use a halitometer or similar devices to measure the concentration of specific gases associated with bad breath. These instruments provide quantitative data for a more objective assessment.
Patient Education:
- Oral Hygiene Instruction: Based on the findings, dental professionals provide tailored oral hygiene instructions to address the specific causes of bad breath. This may include recommendations for brushing, flossing, tongue cleaning, and the use of antimicrobial rinses.
Combining these elements allows dental professionals to assess oral odor during a dental examination comprehensively. This thorough approach identifies underlying issues contributing to bad breath, leading to targeted and effective treatment strategies.