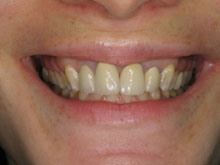
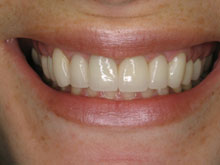
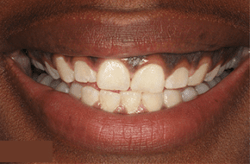
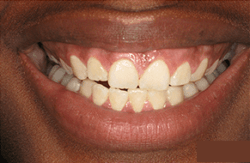
Preventing Gum Disease
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Gum disease is caused by bacteria that thrive in the mouth and produce toxins that can damage the gums and bone that supports the teeth. Gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems if left untreated. Understanding gum disease is important for maintaining good oral and overall health. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease and taking steps to prevent and treat it, individuals can avoid the serious consequences of this common condition.
Preventing and treating gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and visiting one of our dental professionals for professional cleanings and check-ups. If gum disease is detected, we provide several effective treatment options for any case. Treatments include scaling and root planing, Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure (LANAP), medication, or traditional gum surgery in severe cases.
Types of Gum Disease
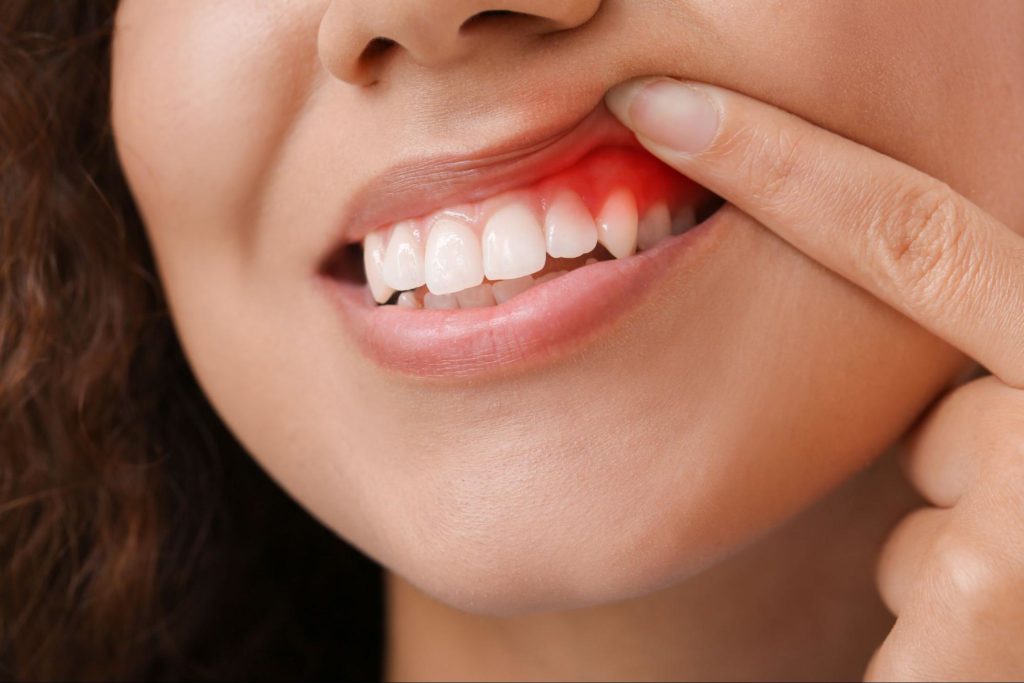

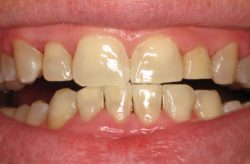
Understanding gum disease involves knowing the different stages of the condition. By knowing the different stages of gum disease, a proper diagnosis and treatment may be given. There are two main types of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the earliest stage of the disease and affects only the gums. It is also the only stage that can be reversed with proper dental care.
Periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease, affecting the gums and the bone supporting the teeth. There are also different types of periodontitis, including mild, moderate, and advanced periodontitis.
Gingivitis
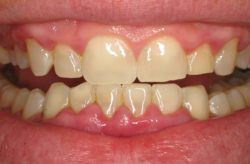
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. It is caused by plaque build-up, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. Gingivitis is reversible with proper dental care, such as regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings by a dental hygienist. When left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a slightly more advanced form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and other health problems. Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs of gingivitis and seek prompt treatment to prevent the condition from progressing.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an advanced form of gum disease that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. During this stage, the build-up of plaque and tartar begins to accumulate below the gum line, which can lead to the formation of pockets and cause infections that can damage the gums and bone.
Symptoms of periodontitis include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and changes in the bite. It is important to recognize the signs of periodontitis and seek prompt treatment to prevent the condition from progressing.
Mild Periodontitis
Mild periodontitis is characterized by a mild form of inflammation in the gums, which can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding. Poor oral hygiene habits typically cause it and can be prevented and treated with proper oral maintenance.
Moderate Periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease than mild periodontitis. Moderate periodontitis also involves damage to the bone and other tissues that support the teeth. One of the key differences between moderate and mild periodontitis is that there are deeper pockets between the teeth and gums, which can harbor bacteria and further destroy the bone and tissues. Common symptoms include gum recession, tooth mobility, and changes in the bite.
Advanced Periodontitis
Advanced periodontitis is known as the most severe stage of gum disease and is irreversible. It is characterized by significant damage to the bone and connective tissue that support the teeth, which can ultimately result in tooth loss. The symptoms of deeper gum pockets, severe gum recession, and loose or shifting teeth.
The Causes of Gum Disease
The main cause of gum disease is the build-up of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth that can harden into tartar if not removed by brushing and flossing. When plaque and tartar accumulate on the teeth and gums, they can cause inflammation and infection, leading to the development of gum disease. Other risk factors for gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and genetic factors. Poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates, and a weakened immune system can also increase the risk of developing gum disease.
Plaque Build-up
Plaque is a soft, sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms on teeth, gums, and other surfaces in the mouth. It is composed of bacteria, saliva, and food particles. If not removed regularly through brushing and flossing, plaque can accumulate on teeth and harden into tartar, which is a hard, yellowish deposit that a dental professional can only remove.
Over time, the bacteria in plaque produce acid, which can damage tooth enamel and cause cavities. Individuals can prevent plaque build-up by practicing good oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice a day properly with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and visiting a dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. In addition to these habits, maintaining a healthy diet low in sugary and acidic foods and beverages can also help prevent plaque build-up.
Poor Oral Hygiene

Poor oral hygiene is one of the main causes of gum disease. When teeth are not cleaned or flossed properly, plaque begins to attach and accumulate on the teeth and gums, causing inflammation, bleeding, and even tooth loss if left untreated. It is important to understand how poor oral hygiene contributes to gum disease and what steps can be taken to prevent it from occurring and progressing.
By practicing good oral hygiene habits and seeking timely treatment, individuals can prevent and manage gum disease, maintaining good oral health for a lifetime. Here are some reasons why practicing good oral hygiene habits is important:
- Prevent Tooth Decay. Brushing and flossing remove the food particles and plaque that can cause tooth decay and cavities. Regular dental check-ups can detect early signs of decay and prevent further damage to the teeth.
- Prevent Gum Disease. Good oral hygiene practices can also prevent gum disease, which can cause inflammation, bleeding, and even tooth loss. Brushing and flossing remove the bacteria that cause gum disease, while regular cleanings can remove the build-up of plaque and tartar.
- Freshen Breath. Proper oral hygiene practices can help to keep your breath fresh by removing the bacteria that cause bad breath.
- Maintain Overall Health. Poor oral hygiene has been linked to other health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Regular dental check-ups can help to detect these problems early on and prevent further health complications.
- Save Money. Good oral hygiene practices can save money in the long run by preventing the need for costly dental procedures such as fillings, root canals, and extractions.
Smoking and its Impact on Gum Health
Smoking is a harmful habit that can negatively affect overall health, including gum health. Smoking can increase the risk of developing gum disease and can make the condition more severe. Here are some ways smoking can impact gum health:
- Reduced Blood Flow. Smoking can reduce blood flow to the gums, preventing them from healing properly and increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Increased Plaque and Tartar Build-up. Smoking can lead to increased plaque and tartar on the teeth, which can contribute to gum disease.
- Weakened Immune System. Smoking can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections such as gum disease.
- Masking Symptoms. Smoking can mask the symptoms of gum disease, making it more difficult to detect and treat early on.
- Slower Healing. Smoking can slow down the healing process after dental procedures, making it more difficult for the gums to recover.
- Increased Risk of Tooth Loss. Smoking can increase the risk of tooth loss due to the damage it can cause to the gums and bone that support the teeth.
Quitting smoking is the best way to prevent its negative effects on gum health. By quitting smoking, individuals can reduce their risk of gum disease, improve blood flow to the gums, and strengthen the immune system.
Genetics
Genetics can play a role in the development of periodontal disease. Research has shown that individuals with a family history of gum disease are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Some ways that genetics can impact gum health include:
- Inherited Immune System. Certain genetic traits can affect the immune system’s response to bacteria in the mouth, making some individuals more susceptible to gum disease.
- Inherited Bone Structure. Genetic factors can influence the structure of the jawbone and gums, making it easier for bacteria to accumulate and contribute to gum disease.
- Inherited Risk Factors. Some individuals may inherit risk factors such as diabetes or a tendency to smoke, which can increase the risk of developing gum disease.
- Inherited Inflammation Responses. Genetic Factors can also affect the body’s inflammatory response, making some individuals more susceptible to inflammation of the gums.
Individuals with a family history of gum disease should take extra care to maintain good oral hygiene practices and inform our dental professionals of their family history to prevent and manage gum disease. If you have a family history of gum disease and want to take preventative steps, call (877) 440-3564 to schedule your appointment.
Medications
Certain medications can have an impact on oral health and may increase the risk of developing gum disease. Some medications that increase the risk of gum disease include:
- Antidepressants: Some types of antidepressants can cause dry mouth, which can increase the risk of gum disease due to lack of saliva.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can also cause dry mouth, leading to an increased risk of gum disease.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Certain blood pressure medications can cause gum overgrowth, making it difficult to keep teeth and gums clean and healthy.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressant medications can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections such as gum disease.
- Chemotherapy Drugs: Chemotherapy drugs can cause a variety of oral health problems, including gum disease, due to their impact on the immune system and oral tissues.
- Oral Contraceptives: Some types of oral contraceptives can increase the risk of gum disease due to changes in hormone levels.
If taking any of these medications, individuals should inform our specialists and take extra care to maintain good oral health. We also recommend these individuals talk to their healthcare providers about any potential side effects of their medications and discuss possible alternatives if necessary.
Health Conditions
Studies have shown that several health conditions can have an impact on gum health and increase the risk of developing gum disease. Some health conditions and their effects on gum health include:
- Diabetes. Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections such as gum disease due to elevated blood sugar levels, which can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections.
- Heart Disease. Research has shown a link between gum disease and an increased risk of heart disease. Both gum disease and cardiovascular disease involve chronic inflammation.
- Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis can cause bone loss in the jaw, contributing to gum disease.
- Pregnancy. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation and infection, leading to an increased risk of gum disease.
Individuals with these health conditions need to take extra care to maintain good oral hygiene habits. Additionally, individuals should inform our specialists of any health conditions they may have and work with their healthcare provider to manage their condition and prevent complications such as gum disease.
Common Symptoms of Gum Disease

Early Signs of Periodontitis
Recognizing the early signs of periodontitis can help prevent the condition from progressing and causing further damage. Early signs and symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Persistent Bad Breath. Bad breath can signify periodontitis, particularly if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as bleeding or receding gums.
- Gum Inflammation. Inflammation of the gums is a common sign of periodontitis. The gums may appear red or swollen and feel tender or painful to touch. There is also slight bleeding present during this stage.
- Gum Recession. As periodontitis progresses, the gums may begin to recede, exposing more of the tooth’s surface. This can cause the teeth to appear longer than normal.
- Tooth Sensitivity. The tooth root may become exposed as the gums recede, leading to tooth sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
- Loose Teeth. The gums and the bone that support the teeth may begin to break down, causing the teeth to become loose or shift in position.
If experiencing any of these symptoms, consult with one of our experienced specialists by calling (877) 440-3564. We will diagnose and effectively treat the case to prevent the gum disease from progressing to its more aggressive stages, causing further damage to the teeth and gums.
Advanced Signs of Periodontitis
When gum disease is left untreated, you are allowing the disease to worsen and progress to a more advanced stage. During the advanced stage of periodontitis, the harmful bacteria begin to affect more areas of the mouth, specifically below the gumline. The symptoms are much more aggressive during this stage. The advanced signs of periodontitis include:
- Tooth Loss. In advanced cases of periodontitis, the bone that supports the teeth may become severely damaged, leading to tooth loss. Teeth that are loose or shift in position are also a sign of advanced periodontitis.
- Deep Pockets. The space between the teeth and gums (known as the gingival sulcus) is shallow in healthy gums. The gingival pockets are greater than 6 millimeters in depth. In advanced cases, these pockets can deepen, allowing the bacteria to accumulate and cause further damage to the gums and bone.
- Receding Gums. The gum recession is much more advanced, and more of the tooth’s root is exposed. Tooth sensitivity is more sensitive during this stage.
- Bone Loss. The bone that supports the teeth begin to deteriorate at a faster rate. This can cause the teeth to become loose and shift in position.
- Abscesses. There is visible pus around the teeth and gums. In severe cases of periodontitis, abscesses may develop between the teeth and gums, which can be a sign of a serious infection.
It is important to see a dental professional as soon as possible when experiencing these symptoms. Our Periodontists will thoroughly examine the gums and teeth to determine the extent of the periodontitis and develop a personalized treatment plan to restore your oral health. Treatments for advanced periodontitis may include deep cleaning, antibiotics, Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure (LANAP), and in severe cases, surgery.
Why Gum Disease is a Serious Health Issue
Gum disease is not just a dental problem but can also seriously affect your overall health. As mentioned earlier, research has shown that gum disease is linked to several chronic health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, diabetes, respiratory disease, and even some types of cancer. This is because the bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, causing systemic inflammation that contributes to these health problems.
Additionally, gum disease can also have a negative impact on pregnancy, Pregnant women with gum disease have an increased risk of premature birth and low birth weight infants.
Furthermore, individuals with gum disease may also experience social and emotional issues, such as anxiety, embarrassment, and low self-esteem due to bad breath, bleeding gums, and tooth loss.
Preventing gum disease is crucial for maintaining good oral and overall health. If you notice any signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, bad breath, or loose teeth, seek dental attention immediately to prevent the condition from worsening. By following these steps, you can prevent and manage gum disease and protect your teeth and overall health.
Prevention is Key: Daily Dental Hygiene Habits
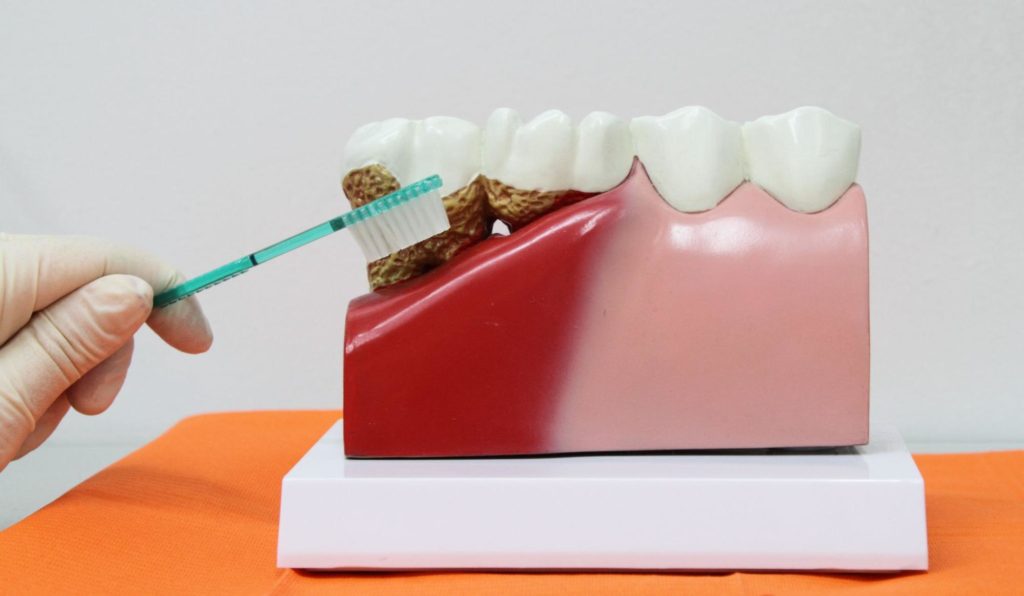
Prevention is key when it comes to gum disease. Gum disease is largely preventable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Here are some reasons why prevention is key for gum disease:
- Prevention Can Save You Money. Treating gum disease can be expensive, especially during its more advanced stages. Prevention, on the other hand, is much cheaper and can save you a lot of money in the long run.
- Prevention Can Save Your Teeth. Advanced gum disease can lead to tooth loss, which can significantly impact your quality of life. By preventing gum disease, you can avoid the need for costly and time-consuming tooth replacement options like implants, dentures, or bridges.
- Prevention Can Improve Your Overall Health. As mentioned earlier, gum disease has been linked to several chronic illnesses. By preventing gum disease, you can reduce your risk of developing these conditions and maintain better overall health.
So, how can you prevent gum disease? Several practices are proven to be effective in preventing gum disease. It’s Simple: practice good oral hygiene, including brushing twice daily, flossing, visiting your dental specialist regularly for check-ups and cleaning, maintaining a healthy diet, and more.
Brushing Techniques for Optimal Gum Health
Brushing your teeth is essential to maintaining good oral hygiene and promoting optimal gum health. However, simply brushing your teeth is not enough. To achieve optimal gum health, it is important to use proper brushing techniques. Some helpful tips for brushing your teeth to promote optimal gum health include:
- Use the Right Toothbrush. Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles and a small head that can reach all areas of your mouth. Hard bristles can damage your gums and cause them to recede.
- Use the Right Amount of Toothpaste. Use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste on your brush. Using too much toothpaste can be abrasive and harm your gums.
- Brush at a 45-Degree Angle. Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to your gums and brush in a circular motion. This helps to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth and gums.
- Brush for at least Two Minutes Twice a Day. Brush your teeth for at least two minutes twice a day. This ensures that all food particles and plaque have been brushed away.
- Don’t Forget to Brush Your Tongue. Bacteria can also accumulate on your tongue, so be sure to brush it as well.
- Use Mouthwash. Mouthwash can help to kill bacteria that cause bad breath and gum disease. Rinse your mouth with mouthwash after brushing.
Flossing for Healthy Gums
Flossing is an essential oral hygiene practice that promotes healthy gums and teeth. It involves cleaning the spaces between teeth and along the gum line using a thin strand of dental floss.
Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles that toothbrushes can’t reach, preventing the build-up of harmful bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria can cause gum disease, tooth decay, and bad breath if left unremoved.
Proper flossing technique is crucial for effective cleaning and preventing damage to the gums. To floss correctly, follow these steps:
- Break off about 18 inches of floss and wind it around your middle fingers, leaving about 1-2 inches of floss to work with.
- Hold the floss tightly between your thumbs and index fingers, and gently slide it between your teeth using a sawing motion.
- Curve the floss around the base of each tooth, making sure to go beneath the gum line. Be gentle to avoid injuring the gum tissue.
- Use a clean section of floss for each tooth, and be sure to remove any debris or plaque build-up.
By incorporating proper flossing techniques into your oral hygiene routine, you can maintain healthy gums and a healthy smile for years to come. Flossing at least once a day, preferably before bedtime is recommended. While flossing, pay attention to any bleeding or discomfort, as these are the early signs of gum disease.
Interdental Brushes and Water Flossers: Additional Cleaning Tools
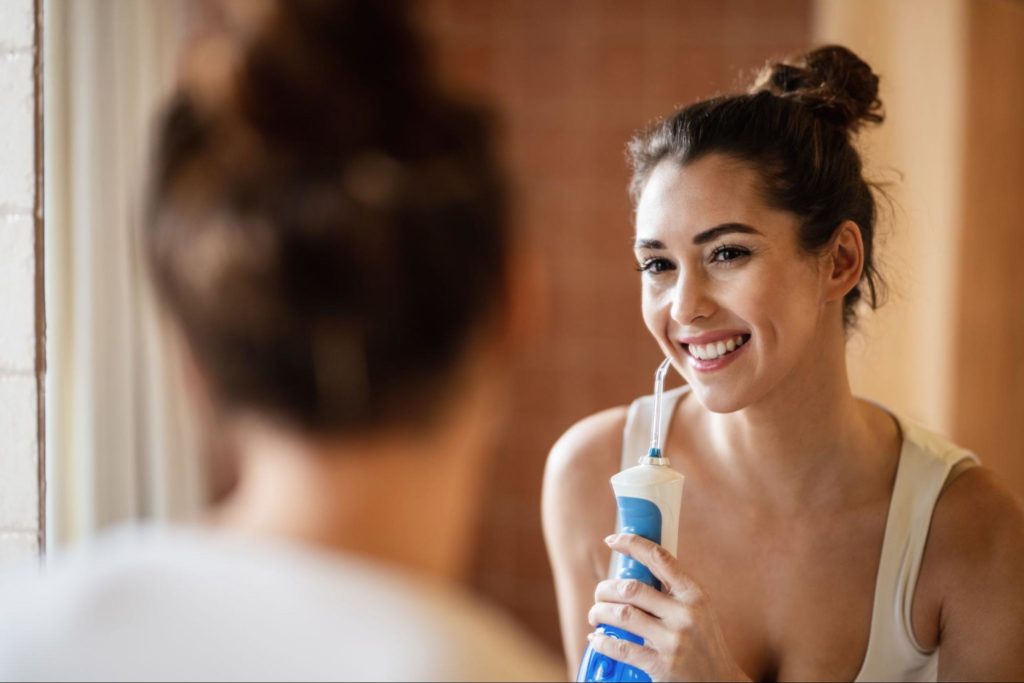

Interdental brushes and water flossers are additional cleaning tools that can be used in conjunction with regular brushing and flossing to promote optimal oral health. They are especially helpful for people with braces, bridges, or dental implants or those who struggle with traditional flossing techniques.
Interdental brushes are small, thin brushes designed to clean the spaces between teeth and the gum line. They come in various sizes to accommodate different tooth spaces and can be reused several times before needing to be replaced. Interdental brushes are easy to use and can be inserted between teeth by gently pushing and pulling them in and out of spaces.
Water flossers, also known as oral irrigators, use a stream of water to remove food particles and bacteria from between teeth and along the gum line. They are effective at removing plaque and reducing the risk of gum disease. Water flossers come in various shapes and sizes and can be used with water alone or with an antibacterial solution.
When using interdental brushes or water flossers, it is important to follow our instructions to avoid injuring the gums or causing discomfort. They are excellent cleaning tools that help prevent gum disease, tooth decay, and bad breath and can be used by people of all ages and dental health levels. They should be used in conjunction with regular brushing and flossing and should not be used as a substitute for these practices.
The Role of a Healthy Diet in Preventing Gum Disease
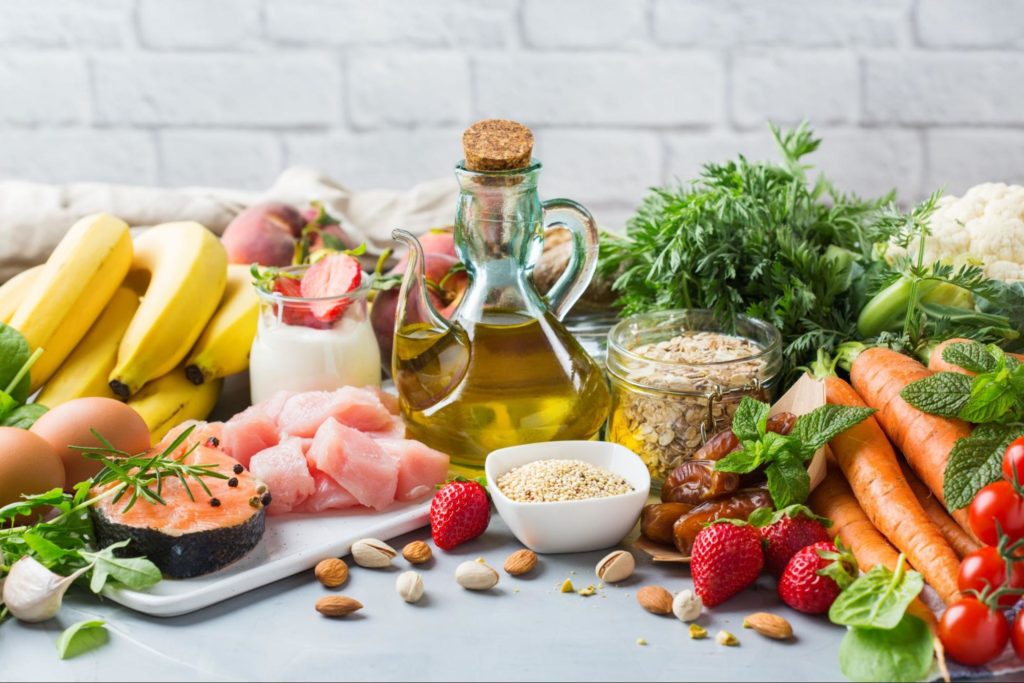

A healthy diet plays an important role in preventing gum disease. A diet high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats can contribute to the development of gum disease, while a diet rich in nutrients can help prevent it.
Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, berries, and leafy green vegetables, can help strengthen the immune system and promote healthy gums. Vitamin C is also essential for producing collagen, a key component of gum tissue.
Foods high in calcium, such as dairy products and fortified foods, can help strengthen teeth and bones, reducing the risk of gum disease. And foods high in antioxidants, such as blueberries, cherries, and green tea, can help reduce inflammation and protect against gum disease.
On the other hand, a diet that is high in sugar and processed foods can contribute to the development of gum disease. Sugar feeds the bacteria in the mouth, leading to an increase in plaque and tartar build-up. Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, contributing to inflammation and gum disease.
Limiting Sugar Intake for Gum Health
Limiting sugar intake is crucial for maintaining healthy gums. Sugar is a primary fuel source for the harmful bacteria in the mouth, which feed on sugars and produce acids that can damage tooth enamel and cause gum disease.
When sugar is consumed, it is broken down into simple sugars like glucose and fructose, which are then metabolized by bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acid as a byproduct of their metabolism, which can dissolve tooth enamel and irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and infection.
To limit sugar intake and promote gum health, it is recommended to:
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks. This includes candies, sweets, soft drinks, and sports drinks, which are high in sugar and can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Choose Healthier Snacks. Opt for fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, and cheese instead of sugary snacks.
- Read Food Labels. Many packaged foods contain hidden sugars, so it’s important to read the labels and choose foods that are low in sugar.
- Use Sugar Substitutes. Sugar substitutes like stevia can be used as a sugar alternative and help reduce gum disease risk.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene. Brush and floss regularly to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums, and visit the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings.
Limiting your sugar intake and practicing good oral hygiene can help prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums and teeth.
The Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining optimal oral health. A dental check-up involves a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and mouth by a dental professional, which can help to detect and prevent dental problems before they become serious.
Our specialists will examine the teeth for signs of decay, cavities, and gum disease during a dental check-up. They will also check the gums for signs of inflammation, bleeding, and recession. We may also take X-rays to check for hidden problems like impacted teeth or bone loss.
Regular dental check-ups can also help to prevent dental problems from developing in the first place. Our specialists can advise on proper brushing and flossing techniques and recommend dental products like toothpaste and mouthwash to help maintain healthy teeth and gums.
In addition, regular dental check-ups can help to detect and treat oral cancer in its early stages. During the check-up, we will examine the mouth for signs of oral cancer, including sores, white or red patches, and any lumps or bumps.
Overall, regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining optimal oral health. They can help detect and prevent dental problems and provide valuable advice on proper oral hygiene and dental products. By scheduling regular check-ups, you can help to ensure that your teeth and gums remain healthy for a lifetime. Call (877) 440-3564 to schedule your next dental check-up with one of our experienced Periodontists here at Laser Periodontics & Gum Surgery.
Understanding the Link Between Gum Disease and Other Health Conditions
Understanding the link between gum disease and other health conditions is important because it highlights the importance of maintaining good oral health for overall health and well-being.
Research has shown that there is a strong association between gum disease and several other health conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, stroke, respiratory disease, and even some forms of cancer.
By understanding the link between gum disease and other health conditions, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage gum disease and reduce their risk of developing other health problems.
Stress and Gum Disease: Managing the Connection
Stress and gum disease are closely connected. When we experience stress, our bodies produce hormones that can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, making it easier for bacteria to grow and cause gum disease. Managing stress can help prevent and manage gum disease.
Managing stress can be challenging, but several strategies can help. One effective way to reduce stress is to practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These practices can help calm the mind and reduce stress hormones in the body.
Another way to manage stress is to engage in physical activity. Exercise can help reduce stress hormones and promote overall health, including oral health. It is also essential to maintain a healthy diet, as eating a balanced diet can help reduce inflammation and improve the immune system.
Suppose you are experiencing stress-related symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, swelling, or pain. In that case, consulting with one of our dental professionals as soon as possible is important. We can provide treatment options, such as dental scaling and root planing (SRP) or antibiotics, to help manage the symptoms and prevent further damage.
Diabetes And Gum Disease
Diabetes and gum disease are closely linked, and people with diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease than those without diabetes. The connection between the two is due to high blood sugar levels, which can lead to inflammation and damage to the blood vessels and nerves that support the gums and teeth.
People with diabetes are also more susceptible to infections, including gum infections, which can make it more difficult for their bodies to fight off bacteria that cause gum disease. Also, gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels, creating a vicious cycle leading to further health problems.
Managing diabetes is essential for preventing and managing gum disease. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, and taking medications as prescribed. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also important for preventing gum disease and catching it early if it does develop.
Gum Disease and Cardiovascular Disease
Gum disease and cardiovascular disease share a close relationship. Several studies have shown that people with gum disease are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, which can lead to heart attack or stroke. The link between gum disease and cardiovascular disease is due to the inflammation caused by the bacteria in the gums, which can travel through the bloodstream and cause damage to the arteries. The inflammation can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
Additionally, gum disease can worsen existing heart disease by increasing inflammation throughout the body and making it more difficult to manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare providers, you can reduce your risk of developing gum disease and cardiovascular disease and promote long-term health.
The Role of Genetics in Gum Disease Prevention
The role of genetics in gum disease prevention is an area of ongoing research and study. While it is clear that genetics can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to gum disease, the exact nature and extent of this role are still being studied.
Research has identified several genetic variations that may increase an individual’s risk of developing gum disease. These variations affect the body’s immune response to the bacteria that cause gum disease and the production of enzymes that break down the connective tissue that supports the teeth.
However, it is important to note that genetics is not the only factor in determining an individual’s risk of gum disease. Environmental and lifestyle factors also play a significant role in gum disease prevention. For example, poor oral hygiene habits, a diet high in sugar and processed foods, and smoking can all increase the risk of gum disease, regardless of genetic factors.
Conversely, practicing good oral hygiene habits, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can all help reduce the risk of gum disease.
Additionally, while genetics may increase an individual’s risk of gum disease, it is not a guarantee that they will develop the condition. With proper oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups, individuals can often prevent or manage gum disease, even if they have a genetic predisposition to the condition.
Therefore, while genetics may play a role in gum disease prevention, it is only one factor contributing to an individual’s risk of developing the condition. Individuals can reduce their risk of gum disease by focusing on a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors and promote long-term oral health and wellness.
Treating Periodontal Disease
Treating periodontal disease typically involves a combination of professional dental treatment and at-home oral hygiene habits. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the condition. Still, it may include scaling and root planing, which involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the root surfaces to prevent further build-up. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to help control the infection.
If periodontal disease has progressed to an advanced stage, surgery may be necessary to remove the deep pockets of bacteria and repair damage to the gums and bone. In some cases, our specialists may use regenerative procedures to help stimulate new bone and tissue growth.
Our Periodontists work one-on-one with patients to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs and goals for oral health. With proper treatment and ongoing care, periodontal disease can be managed and prevented from progressing to more advanced stages.
Professional Dental Cleaning
Professional dental cleanings, also known as dental prophylaxis, are crucial to maintaining optimal oral health. A dental hygienist typically performs these cleanings and involve the removal of plaque and tartar from the teeth, along with other preventative measures.
During a dental cleaning, our hygienist uses specialized tools to remove plaque and tartar, which are bacterial deposits that can accumulate on the teeth and lead to gum disease and tooth decay if left untreated. The cleaning process also includes polishing the teeth to remove surface stains and smooth the tooth surfaces to discourage plaque build-up.
In addition to plaque and tartar removal, dental cleanings also provide an opportunity for the early detection of oral health issues. Our dental hygienist can examine the teeth and gums for any signs of cavities, gum disease, or other dental problems and alert one of our specialists for further evaluation and treatment if needed.
Professional dental cleanings are typically recommended every six months, although the frequency may vary depending on an individual’s oral health needs. Regular cleanings can help prevent gum disease progression, improve oral hygiene, and contribute to better overall health.
As mentioned before, poor oral health has been linked to several systemic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections, highlighting the importance of maintaining regular dental cleanings as part of a comprehensive oral health care routine. Consult with one of our dental professionals by calling (877) 440-3564 for personalized recommendations on the frequency of dental cleanings based on your individual oral health needs.
The Benefits of Professional Teeth Cleaning
Professional teeth cleanings are an important aspect of oral health. Some benefits of professional teeth cleaning include:
- Plaque and Tartar Removal: Despite regular brushing and flossing, plaque (a sticky film of bacteria) can still build up on your teeth, especially in hard-to-reach areas. Over time, plaque can harden into tartar, which a dental professional can only remove. Professional teeth cleanings help remove plaque and tartar, which can prevent cavities, gum disease, and tooth loss.
- Prevention of Gum Disease: Professional teeth cleanings help remove plaque and tartar from the gum line, reducing the risk of gum disease. Regular cleanings can also help detect early signs of gum disease, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further damage.
- Fresher Breath: Bad breath, or halitosis, can be caused by bacteria in the mouth, food particles trapped between teeth, or gum disease. Professional teeth cleanings can help remove bacteria and food debris, resulting in fresher breath and improved oral hygiene.
- Stain Removal: Certain foods, beverages, and habits like smoking can cause stains on your teeth, affecting their appearance. Professional teeth cleanings can help remove surface stains and restore the natural color of your teeth, enhancing your smile.
- Early Detection of Dental Issues: During professional teeth cleaning, our dental hygienist or specialist will thoroughly examine your mouth for any signs of dental issues such as cavities, gum disease, oral cancer, and other dental problems. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, preventing further complications and potentially saving you from more extensive dental procedures in the future.
- Overall Health Benefits: Good oral health is closely linked to overall health. Poor oral hygiene has been associated with various health issues, such as heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Regular dental cleanings can help maintain good oral health, which in turn may contribute to better overall health and well-being.
Regular cleanings and proper oral hygiene practices at home can help keep your teeth and gums healthy and contribute to a brighter, healthier smile. Following our Periodontist’s recommendations for dental cleanings is important as part of your oral health care routine.
Scaling and Root Planing
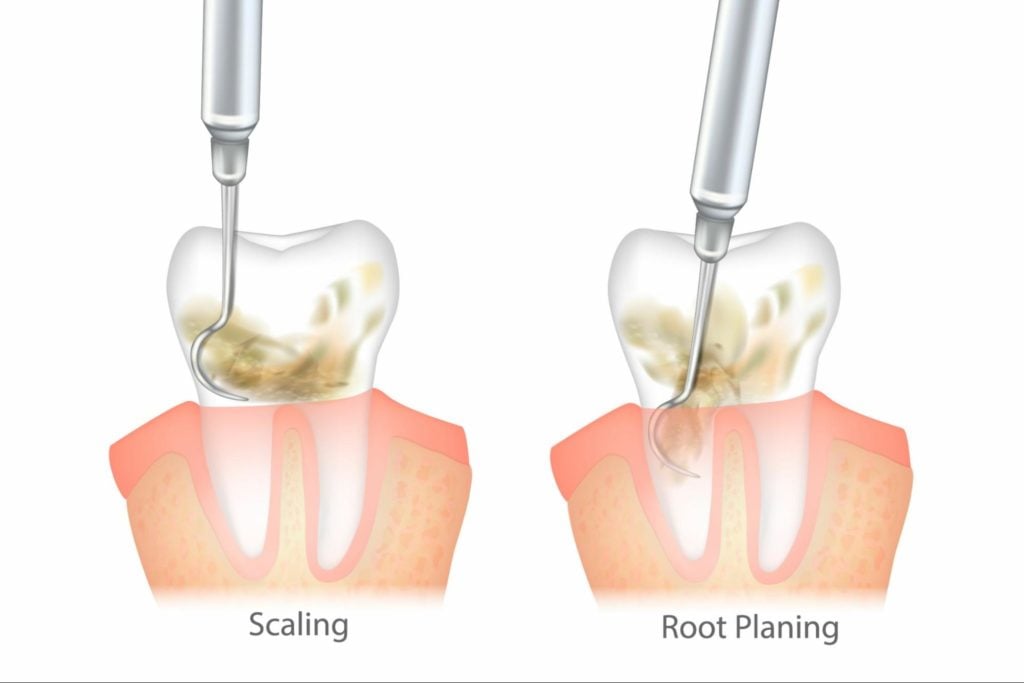
Scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning, is a non-surgical periodontal therapy that involves removing plaque and calculus from the teeth and root surfaces and smoothing out rough areas on the roots. The procedure is typically done under local anesthesia and may be completed in one or more visits, depending on the severity of the gum disease.
Scaling involves the removal of tartar and bacteria from the surfaces of the teeth and below the gumline using specialized tools. Root planing involves smoothing out rough spots and irregularities on the roots of teeth to remove bacteria and promote the healing of the gums.
Scaling and root planing is a highly effective treatment for early to moderate stages of gum disease, also known as gingivitis and periodontitis. It can help reduce inflammation, swelling, bleeding, and pocket depth around the teeth and prevent gum disease progression to more advanced stages.
After the scaling and root planing procedure, we advise our patients to maintain good oral hygiene practices at home, including brushing twice daily, flossing, and regular dental check-ups and cleanings. In some cases, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed to help control infection and promote healing.
Periodontal Surgery
Periodontal surgery is a dental procedure that involves the treatment of advanced periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis. It is a surgical approach to addressing gum disease that has progressed beyond the early stages. It is often necessary when other treatments, such as scaling and root planing, have been unsuccessful.
Periodontal surgery may involve different procedures depending on the gum disease’s severity and the patient’s individual needs. Common procedures include flap surgery, bone grafting, guided tissue regeneration, and soft tissue grafting. These procedures aim to reduce pocket depths around the teeth, regenerate lost bone and tissue, and improve the overall health of the gums and supporting structures.
Periodontal surgery may be done under local anesthesia or sedation, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s preferences. Recovery time varies depending on the procedure and the extent of surgery.
Periodontal surgery can be highly effective in treating advanced gum disease and preventing further damage to the teeth and gums. However, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices at home and schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.
Self-Care Measures
Self-care measures for gum disease include maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and avoiding tobacco use. Incorporating these self-care measures into your daily routine can help prevent and manage gum disease and promote good oral health. A healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in nutrients can also help prevent gum disease. Additionally, stress reduction techniques and regular exercise can promote overall health and reduce inflammation in the body, which can contribute to gum disease.
Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. It involves taking care of your teeth, gums, and mouth by practicing good habits daily. Brushing your teeth twice daily, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help keep your mouth healthy and prevent tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath.
When brushing your teeth, using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush is important to avoid damaging your tooth enamel or gums. You should brush all surfaces of your teeth and your tongue for at least two minutes twice daily. Flossing helps remove the plaque and food particles that get stuck between your teeth, while mouthwash can help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
In addition to regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, it’s important to visit a dental professional for regular check-ups and cleanings. Call (877) 440-3564 to schedule your appointment with one of our highly experienced professionals, and we can help detect and treat oral health problems early before they become more serious.
Quitting Tobacco Use
We understand that quitting tobacco use can be one of the most challenging things a person can do. However, it is also one of the most rewarding. The health benefits of quitting tobacco are numerous and can improve your overall quality of life. Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease. Smoking can also interfere with the healing process of gum tissues after dental treatments.
Quitting tobacco use can help to reduce inflammation and improve blood flow to the gums, which can help to prevent and even reverse gum disease. Quitting tobacco use as soon as possible is important to prevent further damage to your oral health and overall well-being.
The Importance of Taking Action to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease is essential for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. Gum disease is one of the most common dental problems and can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Taking action to prevent gum disease is crucial. This includes:
- Practicing good oral hygiene habits
- Flossing daily
- Using mouthwash
- Visiting your dentist for regular dental check-ups and cleanings for early detection and treatment of gum disease
Individuals can maintain good oral health and reduce the risk of serious health problems by preventing gum disease. It is important to prioritize oral health as part of overall wellness and seek guidance from a dental professional for the best prevention and treatment options.
FAQ
-
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is a serious infection of the gum tissue that can be categorized into three categories based on the symptoms. These stages are gingivitis, periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. The most common symptoms include red and swollen gums, bleeding when brushing and flossing, and deep gum pockets that occur when progressing to the advanced stage of gum disease.
-
What Is Periodontal Maintenance Therapy?
Since periodontal disease is a chronic condition, it is essential to frequently monitor your symptoms to ensure the disease does not reoccur. For patients with a significant amount of periodontal disease, visiting your periodontist or dentist every three months is recommended. Periodontal maintenance is the single most effective treatment to control gum disease.
During this treatment, dental procedures known as scaling and root planing serve to remove plaque, tartar, and calculus from the root surface, as well as from below the gum line. At-home instructions are also given to maintain oral health and prevent disease progression. These sessions are designed to preserve the healthy state of your gums and stabilize your bone levels.
-
Why Is Periodontal Maintenance Therapy Important?
Although there is no cure, gum disease can be managed and controlled with proper oral care and maintenance. While daily oral hygiene certainly helps prevent gum disease progression, it is important to note that this alone will not ensure the termination of bacterial plaque for good. Despite the most thorough flossing, brushing, and use of oral hygiene aids, dental plaque persists to mature in those hard-to-reach places. The growth and maturation of dental plaque after thorough oral care can develop in just 8-12 weeks, returning to damage to the gums and bone. Because of this, it is highly recommended for patients completing periodontal treatment to schedule maintenance sessions every three months. With routine periodontal maintenance visits, our specialists can closely monitor patient oral health differences. We will keep you healthy and smiling!
-
What Is Done During A Periodontal Maintenance Session?
Every patient’s treatment plan is individualized based on their periodontal maintenance session findings. Our specialists will examine the mouth during the session for any noticeable abnormal changes. During the examination, the following will be completed:
- Changes in your health will be discussed
- Pockets will be measured — any changes will be noted
- Your oral hygiene will be evaluated — suggestions will be given regarding how to improve oral hygiene if needed
- Your teeth will be cleaned to remove bacterial plaque and calculus (tartar)
- Necessary X-rays may be taken to evaluate the teeth and supporting bone
- Your teeth will be checked for caries (cavities)
- The bite (the way the teeth fit together) will be checked
-
What is gum disease, and why is it important to prevent it?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth, including the gums and bone. It’s crucial to prevent gum disease because it can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to various systemic health issues, such as heart disease and diabetes. Prevention helps maintain oral and overall health.
-
What are the primary causes of gum disease?
The main causes of gum disease are the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria on your teeth—and poor oral hygiene. Other factors, such as smoking, genetics, health conditions like diabetes, and certain medications, can also increase the risk of gum disease.
-
How can I maintain good oral hygiene to prevent gum disease?
To maintain good oral hygiene and prevent gum disease, you should:
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
– Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth.
– Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in your mouth.
– Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups.
-
Are there specific foods or dietary habits that can help prevent gum disease?
Yes, a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support gum health. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can contribute to gum disease. Drinking plenty of water also helps maintain oral health.
-
How often should I see my dentist for checkups to prevent gum disease?
It is generally recommended to visit your dentist every six months for routine checkups and cleanings. However, your dentist may suggest more frequent visits if you have a higher risk of gum disease or a history of dental problems. Regular dental visits are essential for early detection and prevention of gum disease.
-
Can quitting smoking help prevent gum disease?
Yes, quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease. Smoking weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off gum infections. Additionally, smoking restricts blood flow to the gums, which impairs their ability to heal. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps you can take to protect your gum health.